When To See A Doctor
It is not uncommon for someone with ADPKD to have the condition for years and not know they have it. ADPKD is often diagnosed in people over 30 years of age because symptoms usually dont start before that age.
If you develop signs or symptoms of ADPKD, see your doctor. This is especially important if you have a first-degree relative with the conditiona parent, sibling, or even a child.
How Are Simple Kidney Cysts Treated
In most cases, simple kidney cysts don’t need to be treated. However, if a cyst is putting too much pressure on another organ or is affecting the way a kidney works, it might be necessary to shrink or remove the cyst. There are 2 procedures that are most commonly used to treat simple kidney cysts:
- Aspiration and sclerotherapy: The doctor inserts a long needle under the skin to puncture the cyst and drain the fluid. A strong solution is then injected into the cyst to shrink it. This procedure can be repeated, if necessary.
- Surgery: Surgery to remove a cyst can usually be done laparoscopically, using thin instruments inserted through small holes in the abdomen. During surgery, the doctor first drains the cyst and then cuts or burns away the cyst itself.
What Causes Polycystic Kidney Disease
People who have PKD were born with it. PKD is almost always inherited from a parent or from both parents. People of all genders, ages, races, ethnicities and nationalities can have PKD. Men and women get PKD equally as often. If you have a blood relative with PKD, you are more likely to have PKD or carry the gene that causes it. If you carry the gene that causes PKD but you do not have the disease, you are called a carrier. This is possible with autosomal recessive PKD.
Also Check: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
What Causes Simple Kidney Cysts
Kidney cysts occur when the tube of a nephron begins to get bigger and fill with fluid. Researchers don’t know what causes this to occur, but they do know that simple cysts aren’t inherited. It is believed that injury or microscopic blockages in the tubules may lead to the development of some simple kidney cysts.
Causes Of Kidney Cysts
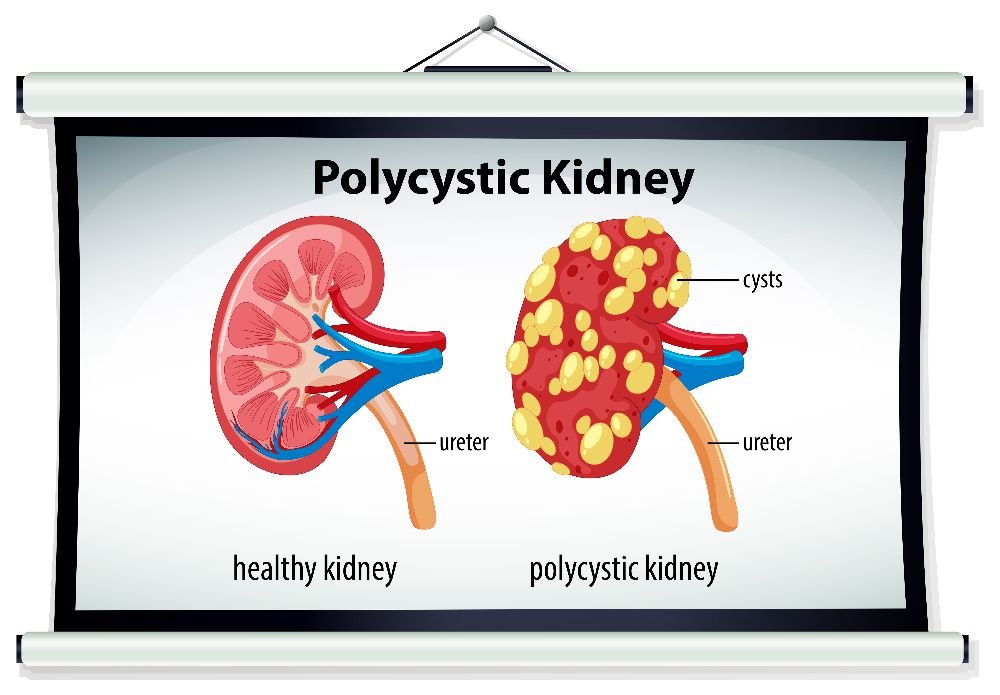
The exact cause of kidney cysts is not fully understood. One theory suggests the kidney cyst develops due to a weak spot on the kidney . The pouch fills with fluid, detaches and thus becomes a cyst.
Another theory believes kidney cysts may be caused due to an obstruction of the tubules, which are related to the collection of urine.
Cysts found in polycystic kidney disease are almost always noncancerous and do not cause many problems. Affected individuals may even go their entire lives without knowing they have the condition. Cysts are thin-walled, small oval, or round sacs filled with watery fluid.
Polycystic kidney disease: A disorder that is characterized by clusters of fluid-filled sacs, called cysts, within the kidney. Cysts may also be found elsewhere in the body. Complications of polycystic kidney disease include high blood pressure, pain, urinary tract infections, liver cysts, and kidney failure due to progressive function loss. Treatment of this disorder often involves managing the complications.
Medullary cystic kidney disease : An inherited condition that can result in cyst formation in the inner part of the kidney called the medulla. This condition often causes kidney failure in people between the ages of 20 to 50.
Medullary sponge kidney: Characterized by cyst development in the urine-collecting ducts and tubules of one or both kidneys. The condition is thought to be mainly inherited, but the exact cause for medullary sponge kidney is not known.
Don’t Miss: Is Honey Good For Kidney
Should People With Pkd Take A Special Diet
At present, no specific diet is known to prevent cysts from developing in patients with PKD. Reducing salt intake helps control blood pressure in PKD patients who have high blood pressure. A diet low in fat and moderate in calories is recommended to maintain a healthy weight. Speak to your doctor or a dietitian about other changes to your diet, such as avoiding caffeine.
What Are Cystic Tumors
Around 5 percent of liver cysts are cystic tumors, which are abnormal growths that have the potential to become cancerous over time. However, most cystic tumors are benign, and only around 5 percent of them become malignant.
Although cystic tumors usually do not cause symptoms, it can be difficult to distinguish between a potentially cancerous tumor and one that is harmless, or benign.
A doctor may order a biopsy to determine if a cystic tumor might be potentially malignant. However, they will often recommend that a person has surgery to completely remove a cystic tumor and ensure that they do not become cancerous.
Don’t Miss: High Blood Pressure Kidney Pain
Does Everyone With Pkd Develop Kidney Failure
No. About 50 percent of people with PKD will have kidney failure by age 60, and about 60 percent will have kidney failure by age 70. People with kidney failure will need dialysis or a kidney transplant. Certain people have an increased risk of kidney failure including:
- men
- patients with high blood pressure
- patients with protein or blood in their urine
- women with high blood pressure who have had more than three pregnancies
Important Facts About Liver Cysts
Liver cysts are not likely to cause symptoms.
Though, when they do occur, the symptoms will most likely manifest as:
- upper abdominal fullness,
- or pain in the liver area.
Read Also: Is Wine Good For Kidney Stones
What Causes Autosomal Recessive Pkd
Like ADPKD, autosomal recessive PKD is an inherited disease. In this case, however, a child may be born with the disease only if both parents are carriers of the gene that causes it. A carrier is someone who has the gene, but does not have the disease. When both parents are carriers of the gene that causes ARPKD, their child has a 1 in 4 chance of being born with ARPKD. The child has a 1 in 2 chance of being a carrier of the gene that causes ARPKD and a 1 in 4 chance of neither having the disease nor being a carrier of the gene. The disease usually does not affect every generation of a family.
Kidney Failure And Transplant Options
One of the most serious complications of PKD is kidney failure. This is when the kidneys are no longer able to:
- filter waste products
- maintain fluid balance
- maintain blood pressure
When this occurs, your doctor will discuss options with you that may include a kidney transplant or dialysis treatments to act as artificial kidneys.
If your doctor does place you on a kidney transplant list, there are several factors that determine your placement. These include your overall health, expected survival, and time you have been on dialysis.
Its also possible that a friend or relative could donate a kidney to you. Because people can live with only one kidney with relatively few complications, this can be an option for families who have a willing donor.
The decision to undergo a kidney transplant or donate a kidney to a person with kidney disease can be a difficult one. Speaking to your nephrologist can help you weigh your options. You can also ask what medications and treatments can help you live as well as possible in the meantime.
According to the University of Iowa, the average kidney transplant will allow kidney function from 10 to 12 years.
You May Like: Can Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
Cysts In Kidney: When To Be Concerned
Many people with simple kidney cysts are asked to have a watchful waiting procedure. In other words, they are usually suggested to periodically take an imaging test to see whether the cysts are still tolerated or the treatment should be taken promptly.
While most of the time cysts in the kidneys are considered harmless and dont require treatment, this could be different when they have caused symptoms and complications.
Although these cysts are usually not serious or even sometime they may go away naturally without treatment, its not always easy to stop worrying about them. In general, the treatment may be suggested if some of the following conditions occur:
What Are The Symptoms Of Simple Kidney Cysts
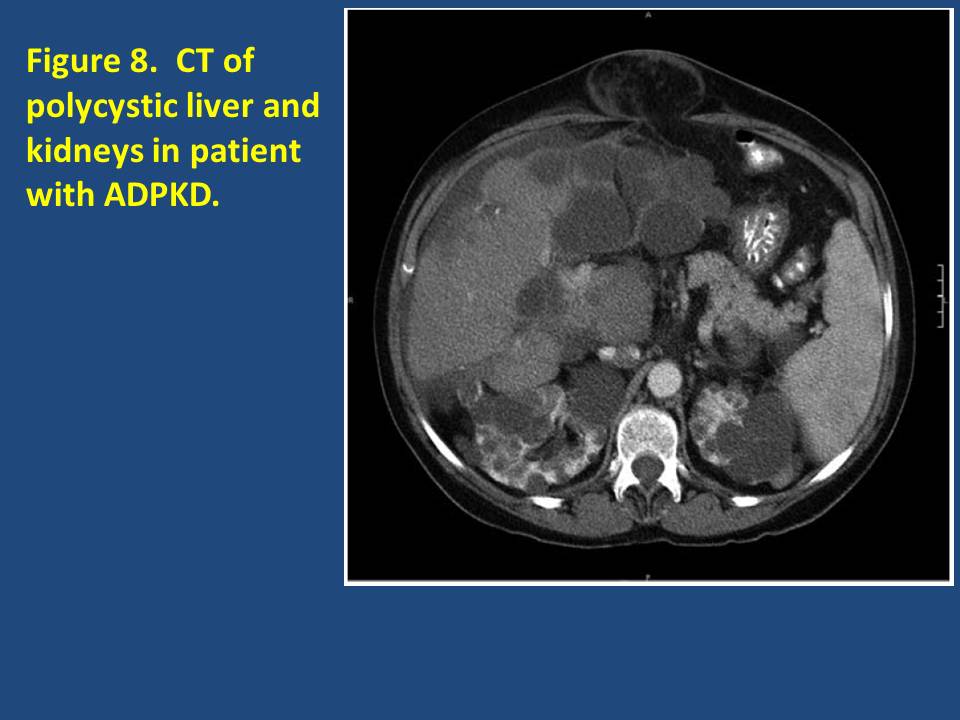
Simple kidney cysts usually don’t cause any symptoms. In fact, most people who have them don’t know they have them. The cysts become a problem if they rupture and start to bleed, become infected, or grow so large that they push against other organs within the abdomen.
When simple kidney cysts do cause symptoms, they might include:
- Pain in the side between the ribs and hip, stomach or back.
Depending on where the cyst is located, it can affect how the kidney works. It can also lead to a type of high blood pressure if the cyst prevents the kidney from filtering extra fluid from the blood.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have 4 Kidneys
What Are The Related Health Complications Of Adpkd
PKD can affect organs other than the kidneys. The following list of potential problems may look long and overwhelming, but it is important to remember that most people do not have all of these problems. If you have PKD, you and your family should be aware of the following possibilities so you can play an active role in understanding and managing your own healthcare.
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
You May Like: Does Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
How Is Pkd Treated
At present, there is no cure for PKD. However, a lot of research is being done. Recent studies suggest that drinking plain water throughout the day and avoiding caffeine in beverages can slow the growth of cysts. Research is also helping us understand the genetic basis of PKD.
Studies also suggest that some treatments may slow the rate of kidney disease in PKD, but further research is needed before these treatments can be used in patients. In the meantime, many supportive treatments can be done to control symptoms, help slow the growth of cysts, and help prevent or slow down the loss of kidney function in people with PKD. These include:
- careful control of blood pressure
- prompt treatment with antibiotics of a bladder or kidney infection
- lots of fluid when blood in the urine is first noted
- medication to control pain
- a healthy lifestyle with regard to smoking cessation, exercise, weight control and reduced salt intake
- drinking lots of plain water throughout the day
- avoiding caffeine in all beverages
In April 2018, the FDA approved a new drug called tolvaptan for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease . The drug can be used to help slow kidney function decline in adults at risk for this type of PKD. You can speak with a healthcare professional for more information about this treatment and if its right for you.
Pathogenesis Of Hepatic Cysts
In the human embryo, the first sign of the bile ducts and the liver is the hepatic diverticulum, also known as the liver bud. For up to 8 weeks of gestation, the extrahepatic biliary tree develops through lengthening of the caudal part of the hepatic diverticulum. This structure is patent from the beginning and as it is, remains in continuity with the developing liver at all stages. The hepatic duct develops from the cranial part of the hepatic diverticulum. The distal portions of the right and left hepatic ducts develop from the extrahepatic ducts and are clearly defined tubular structures by 12 weeks of gestation. The proximal portions of the main hilar ducts derive from the first intrahepatic ductal plates. The extrahepatic bile ducts and the developing intrahepatic biliary tree maintain luminal continuity from the very start of organogenesis throughout further development. The normal development of intrahepatic bile ducts requires finely timed and precisely tuned epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, which proceed from the hilum of the liver toward its periphery along the branches of the developing portal vein. Lack of remodeling of the ductal plate results in the persistence of an excess of embryonic bile duct structures remaining in their primitive ductal plate configuration. This abnormality has been termed the ductal plate malformation .
Also Check: Va Rating For Stage 3 Kidney Disease
Liver Cysts Treatment Tips
Since most liver cysts do not cause symptoms, liver cyst treatment is not necessary. Ultrasound and CT scans are thought to be the best tools for detecting the cysts. Once a cyst is discovered, a doctor will decide whether a biopsy is needed to help determine the type of cyst. Blood tests can rule out a parasite.
Usually, it is only those who show signs and symptoms of liver cysts that require surgical removal of a portion of the cyst wall. Removing fluid from the cyst can be done, but often times it is not all that effective because the cyst just fills back up again. Thankfully, surgical removal is done laparoscopically, which requires just a few small incisions and means the patient will have a quick recovery. When part of the cyst wall is removed, there is little chance of cyst recurrence. When a parasite is the cause of the cyst, antibiotics are a common treatment.
Metformin Slows Liver Cyst Formation And Fibrosis In Experimental Model Of Polycystic Liver Disease
Department of Internal Medicine and Rehabilitation Science, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan
Department of Internal Medicine and Rehabilitation Science, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan
Department of Internal Medicine and Rehabilitation Science, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan
Division of General Medicine and Rehabilitation, Tohoku Medical and Pharmaceutical University Faculty of Medicine, Sendai, Japan
NEW & NOTEWORTHY This study indicates that metformin, an indirect AMPK activator slows liver cyst formation and fibrosis in PLD rat model. Metformin attenuates excessive cell proliferation in the liver with the inactivation of mTOR and ERK pathways. Metformin also reduces the expression of proteins responsible for cystic fluid secretion and liver fibrosis. Metformin and AMPK activators may be potent drugs for polycystic liver disease.
You May Like: Is Honey Good For Kidney
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Liver Disease
PLD is an inherited condition characterized by the presence of multiple scattered cysts of biliary origin throughout the liver parenchyma. PLD occurs not only as an extra-renal manifestation of ADPKD , but also in patients with autosomal dominant PLD , an entity that is genetically distinct from ADPKD and not typically associated with renal cysts .
PLD is classified according to the number, size and the amount of remaining liver parenchyma :
- Type I – unlimited number of large cysts
- Type II – diffuse involvement of the hepatic parenchyma by multiple medium sized cysts with large remaining areas of hepatic parenchyma without cysts
- Type III – diffuse and massive involvement of the hepatic parenchyma by small and medium cysts and only a few areas of normal liver parenchyma between the cysts, the most severe form of the disease.
The gene products of Prkcsh and Esa63, glucosidase II and Sec63p, are located in the endoplasmic reticulum and they are responsible for quality control machinery through which 30% of proteins encoded by the human genome pass, yet heterozygous mutations in these genes manifest only with bile duct cysts indistinguishable from the liver phenotype in ADPKD. Mutations in the Prkcsh and the Sec63 genes solely determine hepatic cyst formation .
Cysts On Liver And Kidney: Should I Be Worried
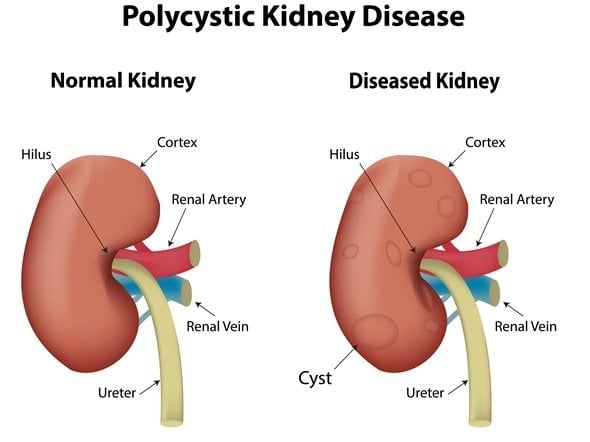
Cyst is normally a benign lesion that is a fluid-filled sac. Those cysts can be found on the kidneys, live, or ovary. Should you be worried if cysts on both live and kidney? Yes, of course.
Get facts on cysts on live
Cysts on liver is also called polycystic live disease, which is one of the complications of Polycystic Kidney Disease .
Polycystic Kidney Disease can cause cysts to develop in other areas of your body besides your kidneys. Cysts in the liver are a common complication, particularly in older people. Around 40-70% of people with ADPKD develop cysts in their liver.
Liver cysts can develop in men and women, but women tend to have more cysts that grow to larger sizes and develop at an earlier age. This is thought to be linked to female hormones, such as oestrogen.
Symptoms of cysts on live and kidneys
1. Abdominal pain
2. Swelling and bloating of your abdomen
3. Yellowing of the eyes and skin
Treatment for cysts on live and kidney
1. In most cases symptoms can be relieved by some medicines prescribed by your doctor. However, long term use of medicines will causes side effects, so you should be careful about the dosage.
2. In rare cases when a larger cyst causes severe and/or persistent pain, surgery may be required to drain the cyst.
3. In very rare cases symptoms becomes too severe to be controlled. When the kidney function is less than 15%, dialysis is required.
Also Check: Can You Have 4 Kidneys