Warning Signs And Symptoms
A kidney stone usually does not cause symptoms until it moves around within the kidney or passes into the ureters. If it becomes lodged in the ureters, it may block the flow of urine causing the kidney to swell and the ureter to spasm. Signs that might likely indicate kidney stones are as follows:
- Severe and sharp pain in the side and back, below the ribs
- Pain that radiates to one side of the back or lower abdomen
- Pain that comes in waves with fluctuating intensity
- Fever and chills, if an infection is present
- Nausea and vomiting
- Intense pain in the abdomen when the stone moves to the ureters
**Nevertheless, some patients may not develop any of these symptoms.
Categories Of Stone Formers
Patients with kidney stones are generally classified in different categories according to the composition of stones and the history of previous stone episodes. This classification influences the diagnostic work up and preventive treatment. However, both of these aspects have limitations. For example, classification according to stone composition has the caveat that chemical methods are imprecise and do not distinguish the crystalline forms infrared spectroscopy or X-ray diffraction are the preferred methods.
We suggest that stone disease should not be evaluated only in reference to stone composition and clinical activity, but the risk of complications should also be appraised in the diagnostic process and patient categorization .
Dont Miss: Is Mulberry Good For Kidneys
Local Population Outcome Studies
In Olmsted County, where one finds Mayo Clinic, Rule and colleagues found an association between development of CKD and a history of kidney stones. This reference is to an extensive review by Rule that lists his own population work and all prior studies he could find prior to 2011. In 2012, Rule established that in Olmsted County kidney stone history associated with eventual need for dialysis. Albeit uncommon, the effect was significant. Finally in 2015, our group reviewed all of the prior evidence concerning this topic of kidney disease, blood pressure, and stones. The conclusion was, as with the work by Rule, that association is undeniable.
Don’t Miss: What Does Calculus In Kidney Mean
Symptoms Of Kidney Stones
Many people with kidney stones have no symptoms. However, some people do get symptoms, which may include:
- a gripping pain in the back usually just below the ribs on one side, radiating around to the front and sometimes towards the groin. The pain may be severe enough to cause nausea and vomiting
- blood in the urine
- cloudy or bad smelling urine
- shivers, sweating and fever if the urine becomes infected
- small stones, like gravel, passing out in the urine, often caused by uric acid stones
- an urgent feeling of needing to urinate, due to a stone at the bladder outlet.
Endocytosis Of Caox Crystals
Various cellular and extracellular events are involved during stone formation. Modulators targeting the steps from supersaturation to crystal retention may be a potential means to block stone formation. Similarly, the blockage of crystal binding molecules expressed on epithelial cell membranes may be an alternative approach to prevent stone formation . Experimental findings demonstrated that stone calcification is triggered by reactive oxygen species and the development of oxidative stress . In vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that CaOx crystals are toxic for renal epithelial cells that produce injury and renal cell death. Similarly, an exposure to hypercalciuria produces cellular injury and ROS-induced lipid peroxidation which stimulates calcium oxalate deposition . The pathophysiology of urinary stone formation is incompletely understood. A summary of the various steps involved in stone formation is shown below .
Schematic representation of the various events of kidney stone formation.
Also Check: How To Avoid Kidney Infection
Kidney Stones And Chronic Kidney Disease
Kidney stones are a formation of hardened minerals in the kidneys or urinary system. In most cases, kidney stones are formed because of a decrease in urine volume or increase in the minerals that form the stones in the urine.
About 1 in every 20 people will have a kidney stone in their lifetime. Three times more men will have kidney stones than women and they are more common in Caucasians. African Americans.
In most cases, kidney stones are formed when there is too little fluid , an overabundance of crystal-forming minerals in the urine, and/or lower-than-normal levels of the chemicals that breakdown these minerals in the urine. The kidney stone will either travel out of the body through the urinary tract or stay in the kidney, bladder or urethra.
Symptoms of kidney stones
You may not know you have a kidney stone unless it causes pain, is large and blocks the flow of urine or is being passed. The most common symptom is severe, fluctuating pain in the lower back or side under the ribs. Other symptoms include:
- Bloody or cloudy urine that smells bad
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Fever and/or chills
- Burning, painful sensation when urinating
If you have symptoms, call your doctor. Taking care of kidney stones early can prevent serious complications, such as chronic kidney disease or, in extreme cases, renal failure that would require dialysis or a kidney transplant to replace the function of the kidneys.
Types of kidney stones and how they are formed
Treatment for kidney stones
Recombination And Genetic Linkage
The diploid nature of chromosomes allows for genes on different chromosomes to or be separated from their homologous pair during sexual reproduction wherein haploid gametes are formed. In this way new combinations of genes can occur in the offspring of a mating pair. Genes on the same chromosome would theoretically never recombine. However, they do, via the cellular process of . During crossover, chromosomes exchange stretches of DNA, effectively shuffling the gene alleles between the chromosomes. This process of chromosomal crossover generally occurs during , a series of cell divisions that creates haploid cells. , particularly in microbial , appears to serve the adaptive function of repair of DNA damages.
The first cytological demonstration of crossing over was performed by Harriet Creighton and in 1931. Their research and experiments on corn provided cytological evidence for the genetic theory that linked genes on paired chromosomes do in fact exchange places from one homolog to the other.
Genes generally their functional effect through the production of , which are complex molecules responsible for most functions in the cell. Proteins are made up of one or more polypeptide chains, each of which is composed of a sequence of , and the DNA sequence of a gene is used to produce a specific . This process begins with the production of an molecule with a sequence matching the genes DNA sequence, a process called .
You May Like: What Breaks Down Kidney Stones
Whats The Outlook For Kidney Stones
The outlook for kidney stones is very positive, although there is a risk of recurrence . Many kidney stones pass on their own over time without needing treatment. Medications and surgical treatments to remove larger kidney stones are generally very successful and involve little recovery time.
Its possible to get kidney stones multiple times throughout your life. If you keep developing kidney stones, your healthcare provider may work with you to discover why the stones happen. Once the cause is found, you may be able to make dietary changes to prevent future stones.
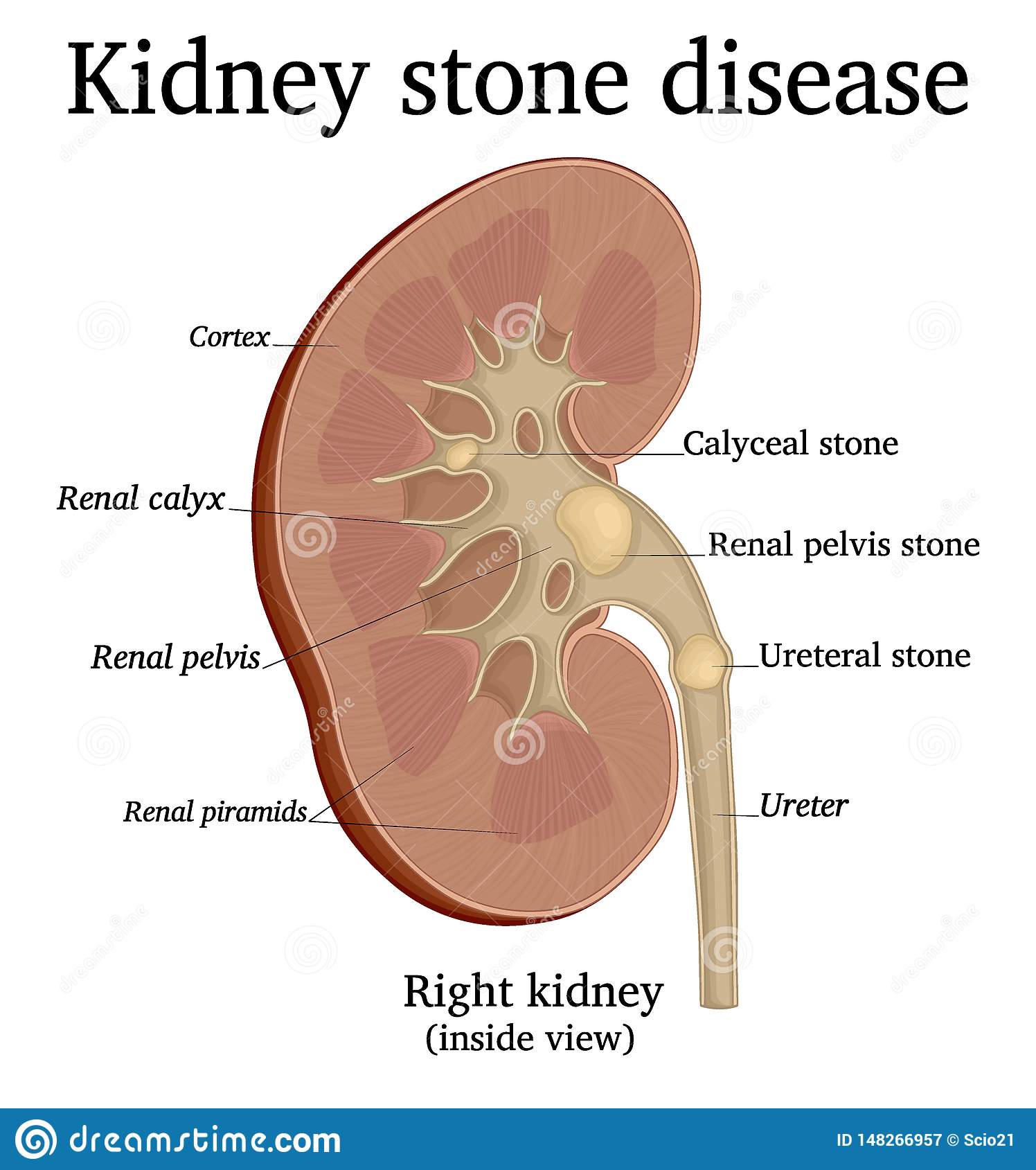
Get To Know Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are defined as hard deposits made of minerals that form inside the kidneys. These stones often form when the urine becomes concentrated, allowing minerals to crystallize and stick together. Kidney stones can affect any part of the urinary tract, extending from the kidneys to bladder. Kidney stones usually range in size from as small as a grain of sand to the size of a golf ball. More importantly, kidney stones can recur after receiving treatments.
Also Check: Is Kidney Disease A Disability
Kidney Disease And Severe Knee Osteoarthritis
If you have kidney problems, it is possible that you will experience aching in various parts of your body. It could be due to an issue with the kidneys, which can cause problems in various parts of the body. Pain in the back, sides, and abdomen are all possible symptoms. This pain could be accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue and nausea. When people with kidney disease experience severe knee osteoarthritis-induced pain, it is likely because of inadequate blood supply. According to a recent study, patients with total knee replacement were significantly more likely to experience severe pain if they had renal insufficiency. This could be due to renal insufficiency, which reduces the bodys ability to produce enough calcium, which can result in severe knee osteoarthritis. If you are experiencing kidney pain, you should seek immediate medical attention.
Dietary Calcium And Kidney Stones
Only lower your calcium intake below that of a normal diet if instructed by your doctor. Decreased calcium intake is only necessary in some cases where absorption of calcium from the bowel is high.
A low-calcium diet has not been shown to be useful in preventing the recurrence of kidney stones and may worsen the problem of weak bones. People with calcium-containing stones may be at greater risk of developing weak bones and osteoporosis. Discuss this risk with your doctor.
You May Like: What Happens If Your Kidneys Shut Down
Prevention Of Recurrent Stone Disease
Many randomized controlled trials have studied dietary or pharmacological interventions to reduce risk of recurrent nephrolithiasis. And, although recommendations to modify different dietary components and to consider selected pharmacological therapy have been included as part of large clinical guidelines on the management of nephrolithiasis,19,20 these guidelines have referenced few of these RCTs.
Dietary therapy for prevention of recurrent stone disease
Pharmacological therapy for prevention of recurrent stone disease
Previous systematic reviews of RCTs of pharmacological therapies have reported that although thiazide diuretics22-24 and citrate therapy24,25 reduce stone recurrence, evidence was insufficient for the efficacy of other pharmacological treatments.22,24,26,27 However, these reviews did not include numerous, more recent RCTs. In addition, these reviews did not evaluate evidence that compared different pharmacological treatments with each other or that compared combinations of pharmacological treatments versus monotherapy, and did not account for baseline fluid and diet intake or fluid and dietary cointerventions. Previous reviews also left unresolved the potential impact of patient demographics, comorbidities, biochemical measures, and stone characteristics on pharmacological treatment outcomes.
Are There Any Foods Or Drinks That Help Treat Kidney Stones Are There Any Home Remedies
There are three liquids rumored to help with kidney stones:
- Cranberry juice. Although cranberry juice can help prevent urinary tract infections , it doesnt help with kidney stones.
- Apple cider vinegar. Vinegar is acidic and it can sometimes create changes to your urine, which helps with kidney stones. But, this doesnt always help. Talk to your healthcare provider about the use of vinegar.
- Lemon juice. Lemon juice is rich in citrate, which can help prevent kidney stones from forming. Citrates are found in several citrus fruits including lemons, limes, oranges and melons.
- Coffee. Studies show that coffee may decrease your risk of developing kidney stones.
Avoid soda and other drinks with added sugar or fructose corn syrup. They increase your risk.
Dont Miss: Can Kidney Disease Cause Osteoporosis
Don’t Miss: What Can Help With Kidney Stones
How Long Does It Take To Pass A Kidney Stone
The amount of time it can take for you to pass a kidney stone is different from anothers. A stone thats smaller than 4 mm may pass within one to two weeks. A stone thats larger than 4 mm could take about two to three weeks to completely pass.
Once the stone reaches the bladder, it typically passes within a few days, but may take longer, especially in an older man with a large prostate. However, pain may subside even if the stone is still in the ureter, so its important to follow up with your healthcare provider if you dont pass the stone within four to six weeks.
F Grading The Evidence For Each Key Question
The overall strength of evidence for the RCTs will be evaluated by using methods developed by the AHRQs Evidence-based Practice Center Program as outlined in the Methods Guide for Effectiveness and Comparative Effectiveness Reviews.35 For each of several important clinical outcomes within each comparison evaluated, the strength of the evidence will be evaluated based on four required domains: 1) risk of bias 2) consistency 3) directness and 4) precision . The risk of biasbased on study design and conductwill be rated low, medium, or high. Consistency will be rated as consistent, inconsistent, or unknown/not applicable . Directness will be rated as either direct or indirect, and precision will be rated as either precise or imprecise. A precise estimate is one that would yield a clinically meaningful conclusion. Other factors that may be considered in assessing strength of evidence include the dose-response relationship, the presence of confounders, the strength of association, and publication bias.
Based on these factors, the overall evidence will be rated as:
Recommended Reading: How To Know If You Have Kidney Problems
What Happens If Kidney Stones Are Left Untreated
Kidney stones can obstruct ureters or make them narrower if left untreated. There is a risk of infection if the urine contains infectious agents, or if the urine contains infectious agents and contributes to kidney strain. Because most kidney stones are treated before they become complications, these conditions are uncommon.
Why You Get Stones
Part of preventing stones is finding out why you get them. Your health care provider will perform tests to find out what is causing this. After finding out why you get stones, your health care provider will give you tips to help stop them from coming back.
Some of the tests he or she may do are listed below.
Medical and Dietary History
Your health care provider will ask questions about your personal and family medical history. He or she may ask if:
- Have you had more than one stone before?
- Has anyone in your family had stones?
- Do you have a medical condition that may increase your chance of having stones, like frequent diarrhea, gout or diabetes?
Knowing your eating habits is also helpful. You may be eating foods that are known to raise the risk of stones. You may also be eating too few foods that protect against stones or not drinking enough fluids.
Understanding your medical, family and dietary history helps your health care provider find out how likely you are to form more stones.
Blood and Urine Tests
Imaging Tests
When a health care provider sees you for the first time and you have had stones before, he or she may want to see recent X-rays or order a new X-ray. They will do this to see if there are any stones in your urinary tract. Imaging tests may be repeated over time to check for stone growth. You may also need this test if you are having pain, hematuria or recurrent infections.
Stone Analysis
Also Check: Can Recurrent Kidney Stones Cause Damage And Why
Can Kidney Stones Cause Kidney Failure
A nephron stone is formed by salts in urine that crystallize. They are sometimes referred to as renal calculi, in addition to their name. Kidney stones can cause infection, kidney damage, and even kidney failure if they obstruct urine flow.
People with rare hereditary disorders are more prone to kidney stones, which can lead to chronic kidney disease . Kidney stones have never been definitively linked to the development of Chronic kidney disease . In Olmsted County, Minnesota, a study was conducted to investigate the prevalence of this condition among residents diagnosed between 1986 and 2003. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of population-based cohort studies to assess the risk of chronic kidney disease associated with kidney stones. Because medical care is self-sufficient within the community, there is a strong population-based foundation for conducting population-based research in Olmsted County. Approximately 95% of the population has at least one clinic visit with a provider every two to three years. Multiple methods for identifying chronic kidney disease were used.
Bladder And Kidney Stones
The feline kidneys have many important functions. Among them are: to filter metabolic waste such as urea, mineral salts, and various toxins from circulating blood to help regulate the volume of body fluids and the blood levels of important chemicals and hormones to initiate the recirculation of purified blood throughout an animals system and to facilitate the excretion of the filtered-out waste products before they reach toxic concentrations in the body. Most cats will go through life without experiencing a serious disruption in these vital processes. Some others, however, will experience urolithiasisa potentially lethal condition marked by the formation of small stones somewhere within this elaborate system.
The upper tract consists of two kidneys, which handle the biochemical processes and two slender tubes one leading from each kidneythat deliver waste-containing urine from the kidneys down to the lower tract. The lower tract, whose function is purely excretory, consists of the bladder, a muscular sac that receives the urine delivered to it through the ureters and stores it until it is expelled from the body via the other component of the lower tract, the urethra, a thin tube leading from the bladder to the outside world. Stones can develop anywhere within either the upper or lower tracts of the urinary system.
Read Also: Can Lemon Water Dissolve Kidney Stones
A Glass Of Wine A Day Ok In Ckd
HealthDay News Drinking a small amount of wine each day is associated with reduced odds of chronic kidney disease and may help protect the heart among those with CKD, according to researchers.
Compared with people who drank no wine at all, those who consumed less than one glass per day had a 37% lower prevalence of CKD , Tapan Mehta, MD, of the University of Colorado-Denver, reported at the National Kidney Foundation Spring 2014 Clinical Meeting.
The association remained significant even after adjusting for demographics, waist circumference, diabetes, hypertension, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides .
Among patients with CKD, those who consumed less than a glass of wine daily were 29% less likely to have cardiovascular disease than non-wine drinkers .
The findings are based on data from 5,852 individuals who participated in 2003-2006 data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, of whom 1,031 had CKD.
Among participants, 2,455 were non-wine drinkers and 27 consumed one or fewer glasses per day, the researchers found. Non-wine drinkers were significantly younger, and had lower prevalence of diabetes and hypertension, higher mean waist circumference, and lower HDL-C levels.
Moderation is the key for kidney patients when it comes to alcohol consumption, the researchers emphasized.
You May Like: How To Find Kidney Failure In Tamil