How Do My Kidneys Filter Blood
Each kidney contains more than a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron consists of:
- Glomeruli: Glomeruli are groups of tiny blood vessels that perform the first stage of filtering your blood. They then pass filtered substances to the renal tubules. The name for this process is glomerular filtration.
- Renal tubules: These tiny tubes reabsorb and return water, nutrients and minerals your body needs . The tubules remove waste, including excess acid and fluids through a process called diffusion. Your body sends the remaining waste through your kidneys collecting chambers. Eventually, it leaves your body as pee.
Secretion Of Active Compounds
The kidneys release several important compounds, including:
- Erythropoietin: This controls erythropoiesis, which is the production of red blood cells. The liver also produces erythropoietin, but the kidneys are its main producers in adults.
- Renin: This enzyme helps manage the expansion of arteries and the volumes of blood plasma, lymph, and interstitial fluid. Lymph is a fluid that contains white blood cells, which support immune activity, and interstitial fluid is the main component of extracellular fluid.
- Calcitriol: This is the hormonally active metabolite of vitamin D. It increases both the amount of calcium that the intestines can absorb and the reabsorption of phosphate in the kidney.
A range of diseases can affect the kidneys. Environmental or medical factors may lead to kidney disease, and they can cause functional and structural problems from birth in some people.
Should I Get Screened
If your wondering if you should get screened you might want to wait. From the article “Screening for chronic kidney disease: which strategy?” Hallan & Stevens 2010 write “Screening for CKD in the general population is still not recommended. However, high-risk groups like patients with diabetes mellitus or hypertension and subjects above age 60 should have their glomerular filtration rate estimated and be tested for albuminuriaâ. If you don’t know if you are at risk you will want to talk to your doctor.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Work Of Kidney In Our Body
What Are The Parts Of The Kidney
Your kidneys are highly complex organs with many parts. The main parts of your kidney anatomy include:
Kidney capsule
The renal capsule consists of three layers of connective tissue or fat that cover your kidneys. It protects your kidneys from injury, increases their stability and connects your kidneys to surrounding tissues.
Renal artery
The renal artery is a large blood vessel that controls blood flow into your kidneys. For most people at rest, the renal kidneys pump a little over 5 cups of blood to your kidneys each minute.
Renal cortex
The outer layer of your kidney, where the nephrons begin. The renal cortex also creates the hormone erythropoietin , which helps make red blood cells in your bone marrow.
Renal medulla
The renal medulla is the inner part of your kidney. It contains most of the nephrons with their glomeruli and renal tubules. The renal tubules carry urine to the renal pelvis.
Renal papilla
These pyramid-shaped structures transfer urine to the ureters. Dehydration and certain medications especially nonsteroidal anti-inflammatorydrugs may damage your renal papilla.
Renal pelvis
This funnel-shaped structure collects urine and passes it down two ureters. Urine travels from the ureters to the bladder, where its stored.
Renal vein
This vein is the main blood vessel that carries filtered blood out of your kidneys and back to your heart. Each of your kidneys has a renal vein.
What Are The Kidneys
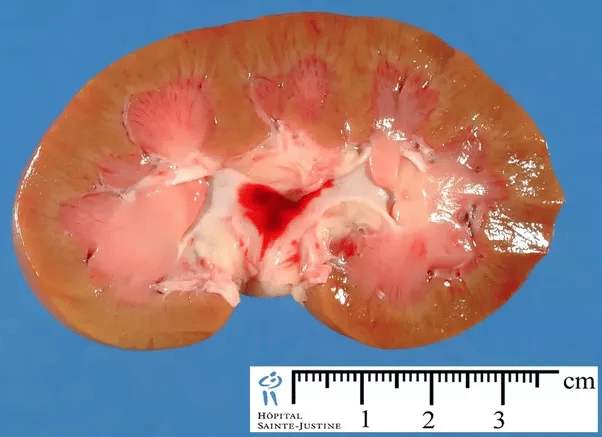
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs that filter your blood. Your kidneys are part of your urinary system.
Your kidneys filter about 200 quarts of fluid every day enough to fill a large bathtub. During this process, your kidneys remove waste, which leaves your body as urine . Most people pee about two quarts daily. Your body re-uses the other 198 quarts of fluid.
Your kidneys also help balance your bodys fluids and electrolytes. Electrolytes are essential minerals that include sodium and potassium.
Also Check: What Do Kidney Stones Feel Like
How Do I Know If Its Kidney Pain
It can be hard to distinguish between kidney pain and back pain.
Back pain is more common than kidney pain. In general, back pain will be related to your muscles, occurs lower in your back, and causes a consistent ache.
If its kidney pain, itll likely be higher, near your ribs. You may feel waves of severe pain and possibly have a fever. The pain may also be stronger on one side.
What Are Common Tests To Check The Health Of My Kidneys
Healthcare providers use several tests to measure kidney function and diagnose kidney problems. Your provider may recommend:
- Advanced imaging: An X-ray, CT scan, MRI, ultrasound or nuclear medicine image can show kidney abnormalities or obstructions .
- Blood tests: Blood tests show how well your glomeruli filter your blood.
- Kidney biopsy: During a kidney biopsy, your healthcare provider removes a small amount of your kidney tissue to examine it under a microscope.
- Ureteroscopy: Your healthcare provider passes a tube through your urethra into your bladder and ureters to look for abnormalities.
- Urinalysis: A urinalysis analyzes your pee. It measures specific substances, such as protein or blood.
Don’t Miss: Can Iud Cause Kidney Infection
What Is Kidney Failure
Kidney failure means one or both kidneys can no longer function well on their own. Sometimes, kidney failure is temporary and comes on quickly. Other times, it is a chronic condition that can get worse slowly over a long time.
Kidney failure may sound serious, and it is. But treatments such as dialysis and kidney transplant help many people with limited kidney function continue to live fulfilling lives.
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
Read Also: Where Is Kidney Stone Back Pain
Keeping Your Kidneys Healthy
Well-functioning kidneys are essential to your overall health. Early detection of kidney disease can be life-saving. Medication and changes to lifestyle, along with an early referral to a kidney specialist, can prevent or delay kidney failure.
If you are at increased risk of chronic kidney disease, talk to your doctor about having a regular kidney health check.
Enlarged Kidney: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Enlarged kidneys are relatively uncommon, with only a few select disorders leading to the condition. The kidneys are responsible for filtering the blood from harmful metabolites and ensuring proper volume status that affects our blood pressure. Having an enlarged kidney will likely compromise all of its function.
Recommended Reading: How To Prepare Beef Kidney Before Cooking
Clinical Relevance: Variation In Arterial Supply To The Kidney
The kidneys present a great variety in arterial supply these variations may be explained by the ascending course of the kidney in the retroperitoneal space, from the original embryological site of formation to the final destination . During this course, the kidneys are supplied by consecutive branches of the iliac vessels and the aorta.
Usually the lower branches become atrophic and vanish while new, higher ones supply the kidney during its ascent. Accessory arteries are common . An accessory artery is any supernumerary artery that reaches the kidney. If a supernumerary artery does not enter the kidney through the hilum, it is called aberrant.
Capillary Network Within The Nephron
The capillary network that originates from the renal arteries supplies the nephron with blood that needs to be filtered. The branch that enters the glomerulus is called the afferent arteriole. The branch that exits the glomerulus is called the efferent arteriole. Within the glomerulus, the network of capillaries is called the glomerular capillary bed. Once the efferent arteriole exits the glomerulus, it forms the peritubular capillary network, which surrounds and interacts with parts of the renal tubule. In cortical nephrons, the peritubular capillary network surrounds the PCT and DCT. In juxtamedullary nephrons, the peritubular capillary network forms a network around the loop of Henle and is called the vasa recta.
You May Like: What Is The Best Diet For Kidney Disease
Measuring How Your Kidneys Work
It is difficult to calculate the exact rate at which your kidneys work. The best measure of kidney function is called the glomerular filtration rate . The GFR can be estimated using a mathematical formula. This formula uses the level of creatinine in your blood to estimate how well your kidneys are filtering waste from your blood. It can indicate if there is any kidney damage.
The higher the filtration rate, the better the kidneys are working. A GFR of 100 mL/min/1.73 m2 is in the normal range. This is about equal to 100 per cent kidney function. Based on this measurement system, a GFR of 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 could be called 50 per cent kidney function and a GFR of 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 could be called 30 per cent kidney function.
If your doctor orders a blood test to learn more about your kidney function, an eGFR result is provided automatically, along with your creatinine results.
Your doctor may also test for other signs and conditions that may indicate you have chronic kidney disease. These may include tests for:
- protein in your urine
- blood in your urine
- high blood pressure
What Is The Current Timeline Of Clinical Trials Why Have There Been Delays
It is difficult to predict timelines due to uncertainties in fundraising, the regulatory process, and technical challenges that can come up along the way. In the best-case scenario, we may be ready to begin the Hemofilter material safety study in 2022. This scenario assumes that we have sufficient funding and no unanticipated scientific, technical, or regulatory drawbacks.
Years ago, when we projected that clinical trials would begin by 2020, it was our most favorable scenario at the time. Our projected timeline has always been dependent on obtaining the required funding, and not encountering unanticipated scientific hurdles.
In 2020, the global community faced the COVID-19 pandemic. Our timeline for starting the first clinical trials was inevitably adversely impacted. Our lab operated at significantly reduced capacity for more than a year. We also faced supply chain interruptions and backlogs at testing facilities. Starting in the summer of 2021, we have been able to resume laboratory activities at full capacity.
We are committed to advancing the development of the bioartificial kidney to patients as quickly as our resources and capabilities allow. We appreciate your patience, understanding, and continued support of The Kidney Project.
You May Like: Is Spicy Food Bad For Kidneys
Why We Need 3d Printed Kidneys
Up to September 2020, there were over 100,000 people in the United States waiting for a kidney transplant. On average, each of these individuals will have to wait 3.6 years for a suitable transplant organ.
In the past 10 years, almost 1,000 children in the UK have been waiting for a kidney. Sixteen under 18s die every year before receiving much-needed transplants.
In a utopian future, patients experiencing kidney failure would simply have a 3D printed kidney made for them in hours. The truth, while fascinating, isnt quite as optimistic as that yet.
Meanwhile, thousands of people are anxiously waiting for a life-saving kidney. The developments in 3D bioprinting technologies arent abstract for them. They are, quite literally, a matter of life and death.
This article covers how 3D printing can be used to create viable human organs, including 3D printed kidneys, and how this bioprinting process works, as well as the likely timescales before this becomes an everyday reality.
Can You Live Without A Kidney
You can live with just one kidney. Healthcare providers may remove one of your kidneys in a radical nephrectomy.
Someone may have only one kidney if they:
- Had a kidney removed due to cancer or injury.
- Made a kidney donation to someone else for a kidney transplant.
- Were born with only one kidney .
- Were born with two kidneys but only one kidney works .
Don’t Miss: How Old Is Too Old For Kidney Transplant
How Are The Cells In The Bioreactor Simultaneously Isolated From The Immune System But Still Kept Alive
The immunoisolation is provided by the membranes on which the cells are grown. The cells are grown on a porous scaffold which allows water, salts, glucose, amino acids, and other very small molecules to pass through it freely. These nourish the cells and allow the cells to dispose of small wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
The immune system relies on fairly large molecules to identify and attach foreign intruders, which are a thousand times larger than, say, glucose. They are too large to penetrate the sieve of the membrane supporting the cells.
Why Did The Kidney Project Partner With Home Dialyzors United And American Association Of Kidney Patients And What Do These Partnerships Mean
In spring of 2017, The Kidney Project announced a new partnership with Home Dialyzors United . In summer of 2018, we partnered with the American Association of Kidney Patients . We are very excited about the opportunities these partnerships bring and see them as important milestones for The Kidney Project.
Partnerships with patient-advocacy groups, such as HDU and AAKP, allow The Kidney Project to access the opinions and the unique perspectives of kidney disease patients, helping to improve the bioartificial kidney device for all users. The FDA encourages medical device developers to incorporate patient perspectives, acknowledging that their voice is often unheard in the medical device development process.
HDU works tirelessly within todays legal and medical systems to advocate for and inform dialysis patients about their options for dialysis care. We have partnered with HDU because of their advocacy experience and their deep understanding of the daily obstacles presented to dialysis patients and their loved ones.
AAKP is the largest kidney patient organization in the country and works closely with Federal government payors, regulators, and quality experts to help officials understand patient needs and risk tolerance. The Kidney Projects partnership with AAKP has allowed us access to AAKPs membership to obtain crucial insights into ESRD patients lived experiences and preferences for next-generation renal replacement therapies.
You May Like: How To Prevent A Uti From Becoming A Kidney Infection
What Do 3d Printed Kidneys Look Like
Getting up close and personal with 3D kidneys is an opportunity few of us will have.
Theres a lot of interest in the technology of 3D bioprinting.
Surgeons and kidney patients are keenly watching developments in this field. Futurists, and anyone who is concerned with questions of human health and medical ethics, will also find value in the progress of 3D printing organs.
Kidneys Are A Filter System
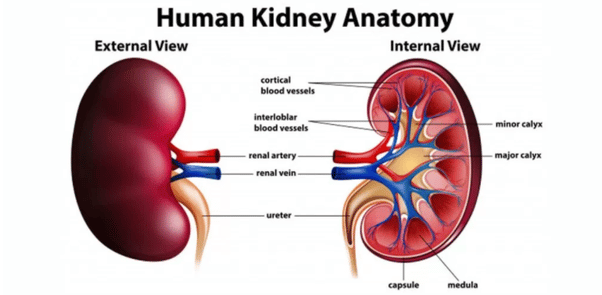
The main job of the kidneys is to remove waste from the blood and return the cleaned blood back to the body. Each minute about one litre of blood one-fifth of all the blood pumped by the heart enters the kidneys through the renal arteries. After the blood is cleaned, it flows back into the body through the renal veins.
Each kidney contains about one million tiny units called nephrons. Each nephron is made up of a very small filter, called a glomerulus, which is attached to a tubule. As blood passes through the nephron, fluid and waste products are filtered out. Much of the fluid is then returned to the blood, while the waste products are concentrated in any extra fluid as urine .
The urine flows through a tube called the ureter into the bladder. Urine passes from the bladder out of the body through a tube called the urethra. The kidney usually makes one to two litres of urine every day depending on your build, how much you drink, the temperature and the amount of exercise you do.
A healthy kidney can greatly increase its work capacity. With two healthy kidneys, each kidney performs 50 per cent of the normal kidney function. If one kidney is lost, the other kidney can enlarge and provide up to 75 per cent of the normal kidney function .
Recommended Reading: Can Stress Affect Your Kidneys
What Can Be Done To Speed Up The Research And Development Process
Our progress is driven by two components: time required to conduct scientific analysis and development, and funding. The scientific analysis and development process cannot necessarily be forced into a faster pace. Because we are developing a novel device and are held to the safety standards of the FDA, we must maintain scientific rigor and technical excellence in a logical order without skipping steps.
However, additional funding allows us to hire more personnel, purchase additional equipment, and generally complete tasks faster. Therefore, donations, investments, and federal funding all help to speed up the research and development process.
Read A Brief Summary Of This Topic
renal system, in humans, organ system that includes the kidneys, where urine is produced, and the ureters, bladder, and urethra for the passage, storage, and voiding of urine.
In many respects the human excretory, or urinary, system resembles those of other mammalian species, but it has its own unique structural and functional characteristics. The terms excretory and urinary emphasize the elimination function of the system. The kidneys, however, both secrete and actively retain within the body certain substances that are as critical to survival as those that are eliminated.
The system contains two kidneys, which control the electrolytecomposition of the blood and eliminate dissolved waste products and excess amounts of other substances from the blood the latter substances are excreted in the urine, which passes from the kidneys to the bladder by way of two thin muscular tubes called the ureters. The bladder is a sac that holds the urine until it is eliminated through the urethra.
Recommended Reading: Is Chronic Kidney Disease Curable