How Is Kidney Pain Treated
The treatment for kidney pain depends on what is causing it. Be sure to call your doctor if you have any kidney pain. Your doctor may do:
- A urine test to check for signs of infection
- Imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or CT scan, to see if your kidneys are injured
Once you know what is causing your pain, your doctor can work with you to find the right treatment.
Webinar
Appetite And Weight Changes
The collective effects of the physical and emotional strain of the disease, its related complications, and its treatments, can wreak havoc on your appetite, which can cause weight changes and further health issues.
- Nausea and vomiting: For those with CKD, nausea and vomiting may include uremic toxin buildup, medications, gastroparesis , peptic ulcers , gastroesophageal reflux disease , and gallbladder disease, among others.
- Loss of appetite: In the early to middle stages of kidney disease, compounds build in the blood that suppresses appetite and can affect your sense of taste. Foods you once enjoyed may start to taste metallic. Depression, anxiety, medications, and other treatments can contribute to appetite loss.
Kidney disease can cause appetite loss, which, in turn, can provoke weight loss.
Upset Stomach Nausea Vomiting
Why this happens:
A severe build-up of wastes in the blood can also cause nausea and vomiting. Loss of appetite can lead to weight loss.
What patients said:
I had a lot of itching, and I was nauseated, throwing up all the time. I couldn’t keep anything down in my stomach.
When I got the nausea, I couldn’t eat and I had a hard time taking my blood pressure pills.
Don’t Miss: Can Kidney Transplant Patients Eat Ginger
Imaging Tests For Kidney Disease
Tests that create various pictures or images may include:
- x-rays to check the size of the kidneys and look for kidney stones
- cystogram a bladder x-ray
- voiding cystourethrogram where the bladder is x-rayed before and after urination
- ultrasound sound waves are bounced off the kidneys to create a picture. Ultrasound may be used to check the size of the kidneys. Kidney stones and blood vessel blockages may be visible on ultrasound
- computed tomography x-rays and digital computer technology are used to create an image of the urinary tract, including the kidneys
- magnetic resonance imaging a strong magnetic field and radio waves are used to create a three-dimensional image of the urinary tract, including the kidneys.
- radionuclide scan.
What Is The Treatment For Acute Kidney Failure
Your treatment will depend on the cause of your acute kidney failure. The goal is to restore normal kidney function. Preventing fluids and wastes from building up in your body while your kidneys recover is important. In the majority of cases, a kidney specialist called a nephrologist makes an evaluation.
Also Check: Apple Cider Vinegar And Cranberry Juice For Kidney Stones
Opioids In Advanced Nondialysis Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease
The degree to which analgesic drug alteration is required for CKD patients largely depends on whether the drug has active metabolites that are dependent on the kidney for excretion. Understanding metabolism of the commonly used analgesic drugs for postoperative pain management helps guide decisions about the type and dose of these agents to be used. Alfentanil and Fentanyl exhibit a safe pharmacological profile for patients with renal impairment. Both are metabolized by the liver producing no active or toxic metabolites. Less than 10% of the parent drug is excreted unchanged in the urine. There is no dose modification required for boluses, but caution is advised with repeated boluses or continuous infusion, as there may be a slight plasma accumulation during advanced stages of renal impairment.
Meperidine is deemed comparatively worse than morphine when considering side effects due to the accumulation of norpethidine, which is a renally excreted neurotoxic metabolite. Patients will be at risk for seizures, especially with repeated doses of meperidine and this drug is, therefore, not recommended for this group of patients.
What Are The Complications Of Mineral And Bone Disorder
The complications of mineral and bone disorder include
- slowed bone growth and bone deformities
- bone fractures
- heart and blood vessel problems
People who experience these complications may have a poorer quality of life, may spend more time in the hospital, and have a higher risk of fractures or death.3
Read Also: Can Kidney Stones Make You Constipated
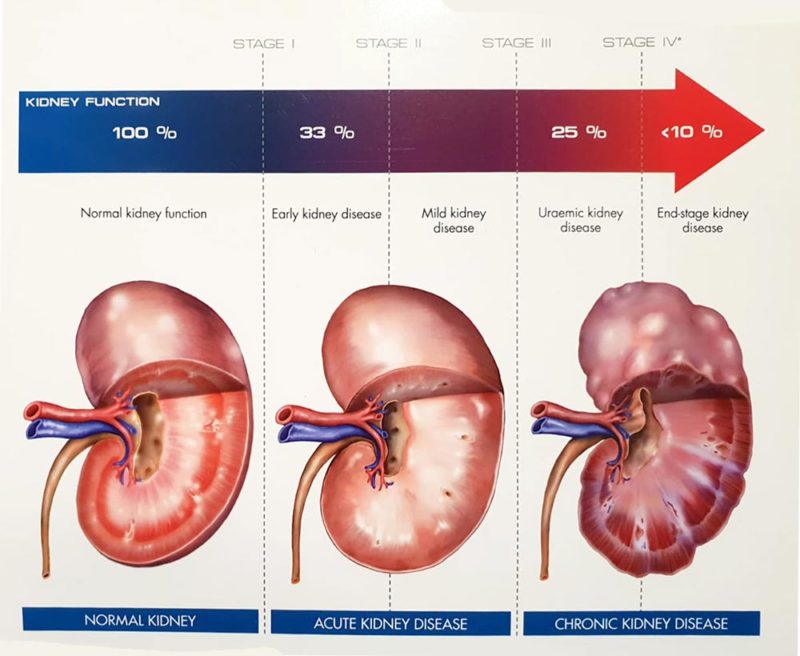
Prognosis Of Chronic Kidney Disease
If chronic kidney disease is caused by a disorder that can be corrected and if that disorder has not been present for too long, then kidney function may improve when the causative disorder is successfully treated. Otherwise, kidney function tends to worsen over time. The rate of decline in kidney function depends somewhat on the underlying disorder causing chronic kidney disease and on how well the disorder is controlled. For example, diabetes and high blood pressure, particularly if poorly controlled, cause kidney function to decline more rapidly. Chronic kidney disease is fatal if not treated.
When the decline in kidney function is severe , survival is usually limited to several months in people who are not treated, but people who are treated with dialysis Dialysis Dialysis is an artificial process for removing waste products and excess fluids from the body, a process that is needed when the kidneys are not functioning properly. There are a number of reasons… read more can live much longer. However, even with dialysis, people with end-stage kidney failure die sooner than people their age who do not have end-stage kidney disease. Most die from heart or blood vessel disorders or infections.
Types And Causes Of Stomach Problems
There are numerous different stomach problems and each can be triggered by different cause. The treatment is determined based on the underlying cause. Therefore its important to diagnose the cause clearly.
The intensity, how it feels like, whether it comes with another symptom, or how long the symptom lasts may help doctors make the diagnosis. Unfortunately, sometime the cause is not known.
Abdominal cramps with diarrhea
One of possible answers is gastroenteritis . The abdominal cramps usually come suddenly, and followed with diarrhea. But the problem is usually harmless or even may improve on its own after a few days.
Gastroenteritis is an infection in the bowel or stomach. Many times, it is caused by getting a close contact with an individual whos infected. It may also occur due to food poisoning or consuming contaminated food.
Another possible cause is irritable bowel syndrome or IBS. This is particularly true if the problem becomes chronic or when you have repeated bouts of abdominal cramps and diarrhea.
Abdominal cramps with bloating
Most of the time, trapped wind is to blame for abdominal cramps with bloating. It is common and easy to deal with but sometime it can be embarrassing, too. It usually improves with over-the-counter such as mebeverine or buscopan.
Recurring, long-term stomach pain
Sometime urinary tract infection such as kidney infection is to blame for this symptom. But it also can be linked to long-term conditions such as:
Sudden severe stomach pain
Also Check: Can Stress Cause Kidney Infection
What Is A Kidney Problem
The kidneys form part of the urinary system, one of the bodyâs major filtration systems. Most people have two kidneys, situated in the upper abdominal area towards the muscles of the back and the edge of the ribs. The kidneys form part of the urinary system along with the two ureters, the bladder and urethra. Kidney problems affect the kidneys, but because the system works together, the effects of a kidney problem are sometimes felt throughout the system.
The kidneys themselves clean the blood by filtering it in the nephrons, which are made up of a renal tubule and a renal corpuscle. The corpuscle is made up of a glomerulus enclosed by the Bowmanâs capsule. To filter the blood, it is passed through the glomeruli at higher pressure than the bodyâs usual blood pressure. Filtered waste products collect inside the Bowmanâs capsule, while filtered, clean blood is passed back out of the glomeruli into the circulatory system. The tubule collects the waste products from the Bowmanâs capsule while also working on further exchanging certain substances and also reabsorbing water and certain minerals so they donât go to waste. The final resulting liquid is then passed into the ureters as urine. Urine collects in the bladder, which stores it until it is released by the urethra.
Read Also: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Other Symptoms Of Bad Kidneys
There are other symptoms that you might not automatically associate with kidney disease, but they are commonly experienced by those living with CKD.
The above list is not exhaustive by any means. It describes some of the most common symptoms that you can expect if the disease progresses to a later stage. If you notice any of the above symptoms, consult with your doctor to explore symptom management options.
Don’t Miss: Is Aleve Bad For Your Kidneys
Pain Management In Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 2
In CKD Stage 2, patients have a mild degree of impairment in renal function . The level of renal function for these patients is sufficient for excretion of the drugs and their metabolites with no need for dose adjustment of pain medications.
There are two main considerations for patients with Stage 2 CKD. Patients should be monitored for further deterioration of renal function due to anesthetic or other perioperative events such as bleeding, dehydration, or prolonged hypotension. Such events that alter renal function may warrant readjustment of the doses for some analgesics. Another important consideration is the possible effect of NSAIDs on the kidney causing further impairment.
Pain Management In End Stage Renal Disease
Postoperative pain management in the nondialysis ESRD patient follows the same rules as delineated for CKD-Stage4. For dialysis dependent patients, the development of the acute-on-chronic pain may also influence the quality of patient care and pain management. Approximately 50% of dialysis patients experience chronic pain that is rated as severe. Chronic pain management for these patients is beyond the scope of this review. Pain can be further complicated by comorbid depression in a high proportion of patients as well as blunted cognitive function which can make interpreting their pain more difficult. Cyclical changes in the plasma concentration of most analgesics before and after dialysis increases the need for dynamic adjustment of doses to balance the risk of toxicity before dialysis and escalation of pain after dialysis.
There is no role for NSAIDS in the postoperative pain management in ESRD due to the high risk of serious side effects in this population . Some exceptions may be accepted for short-term NSAIDs usage in ESRD such as for those patients with acute, painful gout.
Recommended Reading: Orange Juice And Kidneys
The Unexpected Case Of Mrs A
Let us meet Mrs. A, a 58-year-old lady who went for consult because of several episodes of relentless diarrhea and vomiting for four days. She reported that she ate Chinese food the day before she developed the symptoms. She thought that the condition would spontaneously resolve itself, so she did not immediately seek for medical advise. Her appetite started to diminish, and recently, she was unable to go to work. At this point, she was already generally feeling weak. A physical examination was done, and the pertinent medical tests were requested.
For most of us, Mrs. As case may not be considered an uncommon occurrence. In the past, we may have unknowingly eaten spoiled food and suffered from an upset stomach. As we examine this case further, well find how this seemingly common infection caused an unusual complication, and as such, should not have been brushed off so easily.
In order to specify how we ended up with an impression of a simple gastroenteritis, we should first consider other types of diseases from other body systems. From there, we can analyze and safely rule them out as less likely causes.
Summary of body systems and disease classifications that manifest symptoms such as diarrhea and vomiting.
| Body System Involvement |
|---|
Also Check: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Pain Spasms And Other Sensations
Far from only affecting excretion, failing kidney function affects every system, organ, and gland of the body.
Some of the more noticeable symptoms include:
- Pain in the side or mid- to lower back: When only one kidney fails, the pain will occur on the side of the bad kidney. CKD can also cause kidney stones and fluid-filled cysts to develop, which can worsen the pain.
- Muscle cramps and/or twitches: As with athletes, these symptoms are thought to be caused by fluid and electrolyte imbalances, but they also may be the result of nerve damage or blood flow issues.
- Persistently itchy skin: Called pruritus, or uremic pruritus, this may be felt all over the body. It is due to the buildup of wastesespecially excess phosphorusthat the kidneys can no longer filter out. Pruritus is common in end-stage kidney disease .
- Feeling cold all the time: This is a symptom of anemia.
You May Like: Is Vinegar Good For Kidneys
What Is Mineral And Bone Disorder In Chronic Kidney Disease
Mineral and bone disorder in chronic kidney disease is a disorder that can affect the bones, heart, and blood vessels of a person with CKD. Mineral and bone disease occurs when kidneys damaged by CKD cant filter blood and regulate hormones the way they should. The hormone levels and levels of minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus, then become imbalanced, leading to damage.
How Can I Slow Down The Damage To My Kidneys
Healthy life changes can make a big difference in how you feel and can help keep your kidneys working well for as long as possible. Eating kidney-friendly foods in the right amounts is one of the best ways to slow the damage to your kidneys from CKD and to feel your best. A dietitian is a nutrition expert who can look at results from your lab tests and help you plan healthy meals and snacks you’ll want to eat: your “kidney diet.”
Here are other healthy changes that will help slow the damage to your kidneys:
- Be active for at least 30 minutes on most days of the week. This can be anything from walking or riding a bike to swimming or dancing.
- If you have diabetes, follow your treatment plan to keep your blood sugar within your target range.
- Quit smoking or using tobacco.
Also Check: Tea Good For Kidneys
What Is Kidney Dialysis
Because there is no cure for CKD, if you are in late-stage disease, you and your healthcare team must consider additional options. Complete kidney failure, left untreated, will result in death. Options for end stages of CKD include dialysis and kidney transplantation.
Dialysis is a procedure that uses machines to remove waste products from your body when your kidneys are no longer able to perform this function. There are two major types of dialysis.
Hemodialysis: With hemodialysis, your blood is circulated through a machine that removes waste products, excess water and excess salt. The blood is then returned to your body. Hemodialysis requires three to four hours, three times a week and is performed at a clinic, hospital or dialysis center.
Peritoneal dialysis: In peritoneal dialysis, a dialysis solution is run directly into your abdomen. The solution absorbs waste and then is removed via catheter. Fresh solution is added to continue the process of cleaning. You can perform this type of dialysis yourself. There are two types of peritoneal dialysis: continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis , which involves a change in dialysis solution four times a day and continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis . CCPD uses a machine to automatically fill, remove wastes, and refill the fluid during the nighttime.
Can Chronic Kidney Disease Be Prevented
Chronic kidney disease cannot be prevented in most situations. The patient may be able to protect their kidneys from damage, or slow the progression of the disease by controlling their underlying conditions such as diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure.
- Kidney disease is usually advanced by the time symptoms appear. If a patient is at high risk of developing chronic kidney disease, they should see their doctor as recommended for screening tests.
- If a patient has a chronic condition such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, they should follow the treatment recommendations of their health care practitioner. The patient should see their health care practitioner regularly for monitoring. Aggressive treatment of these diseases is essential.
- The patient should avoid exposure to drugs especially NSAIDs , chemicals, and other toxic substances as much as possible.
You May Like: Is Wine Bad For Kidney Stones
What Is Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of the abdominal cavity as the dialysis filter to rid the body of waste and to balance electrolyte levels. A catheter is placed in the abdominal cavity through the abdominal wall by a surgeon, and it is expected to remain in place for the long term. The dialysis solution is then dripped in through the catheter and left in the abdominal cavity for a few hours after which, it is drained out. During that time, waste products leech from the blood flowing through the lining of the abdomen and attach themselves to the fluid that has been instilled by the catheters. Often, patients instill the dialysate fluid before bedtime and drain it in the morning.
There are benefits and complications for each type of dialysis. Not every patient can choose which type he or she would prefer. The treatment decision depends on the patient’s illness and their past medical history along with other issues. Usually, the nephrologist will have a long discussion with the patient and family to decide what will be the best option available.
Dialysis is lifesaving. Without it, patients whose kidneys no longer function would die relatively quickly due to electrolyte abnormalities and the buildup of toxins in the bloodstream. Patients may live many years with dialysis but other underlying and associated illnesses often are the cause of death.