Postoperative And Rehabilitation Care
Follow-up care is a matter of personal preference and will depend on the type of repair performed. If a distal ureteral injury is repaired with reimplantation into the bladder, and a cystotomy is required, a Foley catheter should be left in place postoperatively for 7 to 10 days. Sources vary on the length of time a ureteral stent should be left in place. Some sources recommend keeping the stent in place for up to 6 weeks others advocate removal after 14 days. This is up to the discretion of the practitioner. At the time of stent removal, an RPG can be obtained to document healing without leakage or stenosis. Continued follow up with renal ultrasounds to ensure no restenosis of the ureter occurs is recommended.
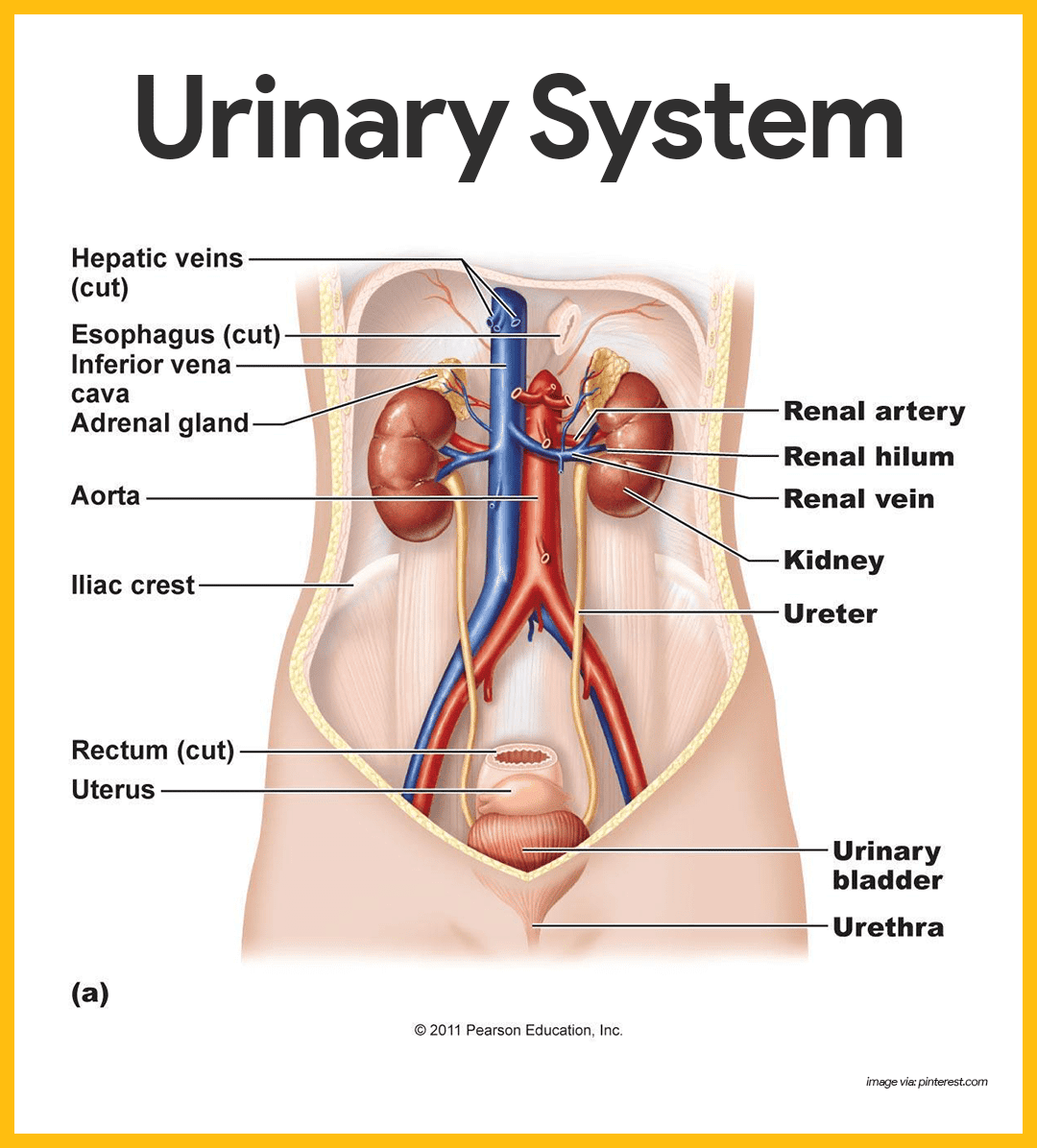
Where Does The Ureters Lead To
The urine travels from the kidneys to the bladder in two thin tubes called ureters. The ureters are about 8 to 10 inches long. Muscles in the ureter walls tighten and relax to force urine down and away from the kidneys. Small amounts of urine flow from the ureters into the bladder about every 10 to 15 seconds.
What Are The Parts Of Ureter
The ureter is 25-30 cm long and has three parts:
- abdominal ureter: from the renal pelvis to the pelvic brim.
- pelvic ureter: from the pelvic brim to the bladder.
- intravesical or intramural ureter: within the bladder wall.
Where is the ureter located in the body?
Ureters connect the kidneys to the bladder. The upper half of each ureter is located in the abdomen and the lower half is in the pelvis. They are approximately 20 to 30 centimeters long in adults.
Read Also: Can Mineral Water Cause Kidney Stones
Blood And Lymphatic Supply
The arteries which supply the ureter vary along its course. The upper third of the ureter, closest to the kidney, is supplied by the renal arteries. The middle part of the ureter is supplied by the common iliac arteries, direct branches from the abdominal aorta, and gonadal arteries the gonadal arteries being the testicular artery in men and the ovarian artery in women. The lower third of the ureter, closest to the bladder, is supplied by branches from the internal iliac arteries, mainly the superior and inferior vesical arteries. The arterial supply can be variable, with arteries that contribute include the middle rectal artery, branches directly from the aorta, and, in women, the uterine and vaginal arteries.
The arteries that supply the ureters end in a network of vessels within the adventitia of the ureters. There are many connections between the arteries of the ureter, particularly in the adventitia, which means damage to a single vessel does not compromise the blood supply of the ureter. Venous drainage mostly parallels that of the arterial supply that is, it begins as a network of smaller veins in the adventitia with the renal veins draining the upper ureters, and the vesicular and gonadal veins draining the lower ureters.
Anatomy Of Adrenal Gland
The adrenal glands of rats are a pair of pale organs lying within the peri-renal fat, cranial to the kidneys. In rats, the right adrenal gland is bean-like in shape and the left adrenal gland is ovoid. Each gland consists of a cortex and medulla and is encased by a connective tissue capsule. The cortex is further divided into three major zones. The outer zone, the zona glomerulosa , is a thin, distinct band of cells arranged in cords and arcs, and is responsible for production of mineralocorticoid hormones, predominantly aldosterone. The middle zone, the zona fasciculata , is generally the largest and most prominent zone. It is composed of cells arranged in long radiating cords or columns, and is responsible for the production of glucocorticoid hormones. The inner zone, the zona reticularis , lies adjacent to the medulla and is primarily responsible for androgen production in mammals. The ZR is composed of cells that are smaller than those in the ZF, arranged in loose cords or trabeculae. The primary function of the ZR in mammals is androgen production however, studies in rats have shown that cells of the ZR do not produce androgen, but do retain the capacity for trace glucocorticoid production .
Fernando J. Kim MD, FACS, Mario F. ChammasJr. MD, in, 2009
Recommended Reading: How Can Your Kidneys Get Damaged
How Can I Keep My Peritubular Capillaries Healthy
You may not always be able to prevent damage to your peritubular capillaries. But you can lower your risk of kidney problems and other health conditions by focusing on staying healthy overall. This includes:
- Eating a balanced diet and drinking water when youre thirsty.
- Managing diabetes, high blood pressure and other chronic health conditions.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and losing weight if you have obesity.
- Quitting smoking since smoking damages all of your blood vessels and causes vascular disease.
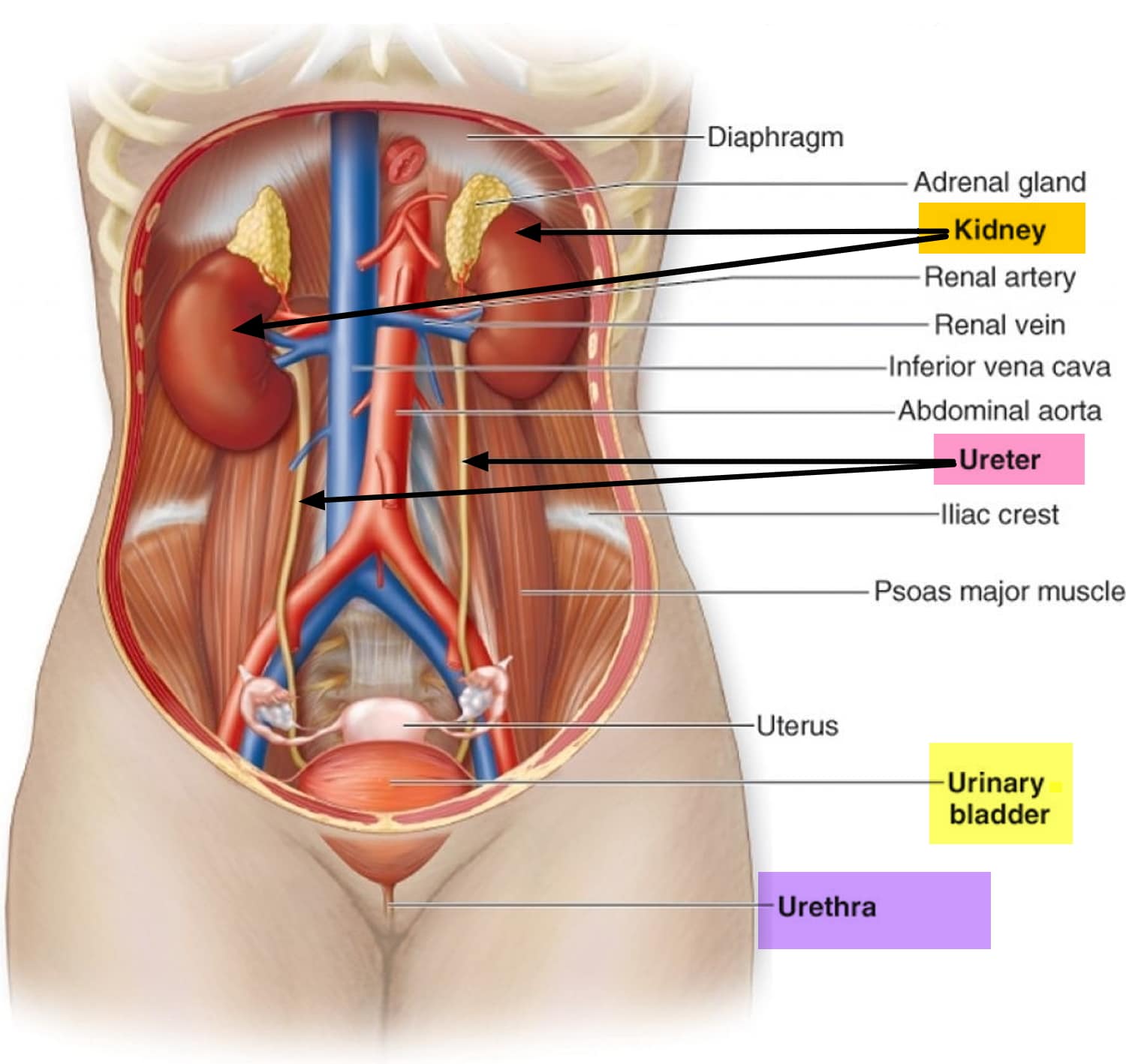
Is The Ureter Attached To The Kidney
The ureter is a tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. There are two ureters, one attached to each kidney. The upper half of the ureter is located in the abdomen and the lower half is located in the pelvic area.
What attaches the kidneys to the Retroperitoneum?
The T12 and L3 vertebrae attach the kidneys to the retroperitoneum.
Where is the urethra and ureter located?
What Are the Ureter and Urethra? The ureter is a small tube, or duct, that connects the bladder and kidneys. Urine passes through the ureter from the kidneys to the bladder. The urethra is the tubular path that connects the bladder to the bodys exterior, allowing urine to exit the body.
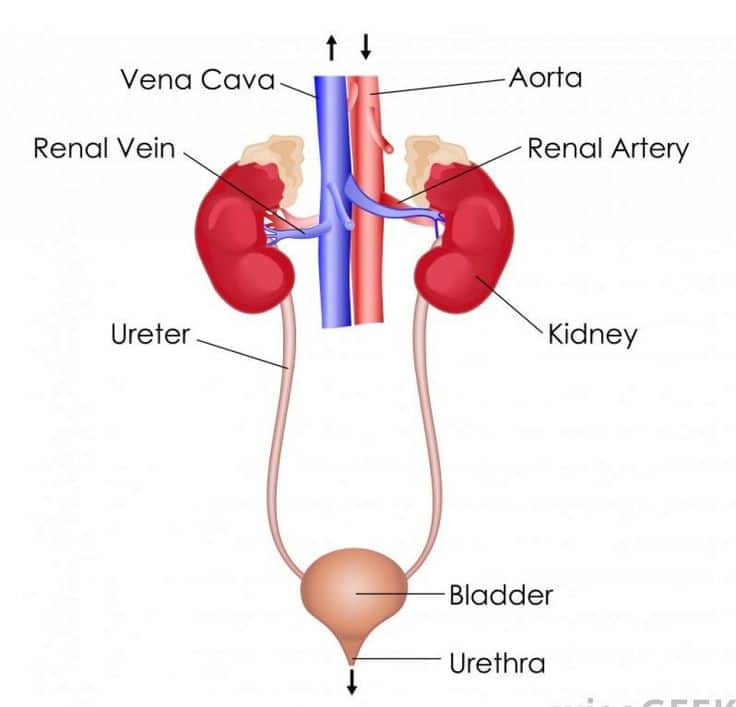
What blood vessels receives blood from the renal veins?
The renal veins are veins that drain the kidney. They connect the kidney to the inferior vena cava. They carry the blood filtered by the kidney.
| Renal vein |
|---|
Also Check: How Long Can You Live With Total Kidney Failure
What Are The Different Types Of Renal Hilum Trauma
The main renal vessels can be interrupted by thrombosis or avulsion. In both instances, there will be no contrast enhancing the injured kidney in the CAT scan with IV contrast. Hematuria may not be present in these cases. The renal artery injury is often stretched with blunt trauma and an intimal flap may cause obstruction and ischemia. Main renal artery trauma with intimal flap can be successfully managed with arterial endovascular stent placement by interventional radiology.
How Do You Evaluate And Identify An Ureteral Injury
The site and mechanism of trauma should prompt the surgeon to suspect ureteral injury. The clinical manifestations are characteristically subtle and often obscured by coexisting injury and complaints. The majority of SWs and GSWs would also injure bowel, colon, liver, spleen, blood vessels, or pancreas. Hematuria is often microscopic, but it may be absent. Extravasation of contrast may be detected with noninvasive and invasive imaging studies. If ureteral injury is suspected during laparotomy, indigo carmine should be given to identify the site of leakage .
You May Like: Did George Lopez Have A Kidney Transplant
How Do You Manage An Unexpected Retroperitoneal Bleeding During Surgical Exploration
A pulsatile hematoma suggests a major vascular injury, and exploration should be preceded by vascular control and preparation for rapid blood replacement. Stable hematomas may be left undisturbed unless studies disclose severe renal damage. When doubt exists, exploration is justified, with the likelihood of losing a kidney.
What Is Conservative Treatment Of Traumatic Renal Injuries
Bedrest until gross hematuria is improved. Drainage of the bladder in cases of urinary extravasation. Monitoring of vital signs, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and urinary output. After hospital discharge, microscopic hematuria can take months to resolve. Blood pressure should be monitored, and urine analysis. Follow-up imaging should be considered for symptomatic patients and/or high-grade renal injury.
Don’t Miss: Can You Reverse Kidney Disease
Where Does The Ureter Penetrate The Kidney Quizlet
Where does the ureter penetrate the kidney? The ureter, blood vessels, and nerves penetrate the kidney on its medial surface. The fibrous capsule is a layer of adipose tissue that surrounds the kidney.
Where is the renal vein located in the kidney?
The renal veins lie ventral to the renal arteries. The left is longer than the right and passes in front of the aorta, just inferior to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery. The renal veins enter the vena cava around the level of L1-L2. The left renal vein is usually slightly more cephalad than the right.
What Are The Treatment Options For Urinary Leakage After Renal Trauma
Urinary extravasation usually does not require surgical intervention. Initially these patients should be managed with bladder drainage to decompress the upper urinary tract. In cases of penetrating injury and gunshot trauma, the ureter can suffer a blast effect that can result in delayed urine extravasation in 48â72 hours, with urinoma formation. In these cases, ureteral stents with or without percutaneous drainage of the urine collection can effectively manage this injury. Surgical repair should be reserved for patients who failed minimally invasive treatments.
Don’t Miss: Do Kidney Stones Hurt When You Move
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A urologist usually manages ureteral injuries, but the cause of ureteral injury can occur during a variety of surgical procedures. An iatrogenic ureteral injury most commonly occurs during gynecologic surgery . Hysterectomy accounts for the majority of cases resulting in ureteral injury. Injury occurs in the distal ureter in the region of the infundibulopelvic ligament, where the ureters cross inferior to the uterine artery. If an injury occurs during laparoscopic gynecologic surgery, it is usually caused by cauterization or clipping.
Ureteral injury also occurs in colorectal and vascular surgery cases. Low anterior resection and abdominal perineal resection account for the majority of colorectal procedures resulting in ureteral injury. In these cases, the left ureter is most commonly injured as it may be elevated with the sigmoid mesentery and mistaken as a mesenteric vessel. Ureteral manipulation is common with aortoiliac and aortofemoral bypass surgery, and thus these surgeries also have a risk for ureteral injury.
It is vital to be aware of a ureteral injury and call the urologist when it occurs. The surgical nurse assistant or scrub nurse should try and remind the surgeons of a ureteral stent in high-risk cases. The type of repair procedure depends on the site and extent of the injury. Untreated ureteral injuries have very high morbidity. Urology nurses monitor patients, provide education during the stay and at discharge, and document for the team. [Level 5)
What Color Is Urine When Your Kidneys Are Failing
When kidneys are failing, the increased concentration and accumulation of substances in urine lead to a darker color which may be brown, red or purple. The color change is due to abnormal protein or sugar, high levels of red and white blood cells, and high numbers of tube-shaped particles called cellular casts.
You May Like: Does Metformin Cause Kidney Damage
How Is Renal Trauma Managed
Hemodynamically stable patients with blunt renal injury can be managed nonoperatively in 98% of cases. Unstable patients with high-grade renal trauma and patients with severe urine leakage or lack of clinical progression are more prone to renal exploration. Arterial stent placement and segmental embolization of the kidney can be performed successfully by interventional radiologists and a moderate urine leak may be treated with ureteral stents.
What Are The Different Types Of Renal Pedicle Trauma
The renal pedicle may be interrupted by thrombosis or complete avulsion both events are characterized by urographic nonvisualization and minimal hematuria. The most common site of arterial interruption is the junction of the proximal and middle thirds of the main renal artery. Although hematuria is often absent, one may see transitory gross hematuria or microhematuria, emphasizing the requirement for urinalysis in all circumstances.
Also Check: How Does Potassium Affect The Kidneys
Kidneys: The Main Osmoregulatory Organ
The kidneys, illustrated in Figure 22.4, are a pair of bean-shaped structures that are located just below and posterior to the liver in the peritoneal cavity. The adrenal glands sit on top of each kidney and are also called the suprarenal glands. Kidneys filter blood and purify it. All the blood in the human body is filtered many times a day by the kidneys these organs use up almost 25 percent of the oxygen absorbed through the lungs to perform this function. Oxygen allows the kidney cells to efficiently manufacture chemical energy in the form of ATP through aerobic respiration. The filtrate coming out of the kidneys is called urine.
What Are The Signs That Something Is Wrong With Your Kidneys
Signs of Kidney Disease
- You’re more tired, have less energy or are having trouble concentrating. …
- You’re having trouble sleeping. …
- You have dry and itchy skin. …
- You feel the need to urinate more often. …
- You see blood in your urine. …
- Your urine is foamy. …
- You’re experiencing persistent puffiness around your eyes.
Don’t Miss: How To Reverse Kidney Disease Naturally
What Keeps The Kidneys In Place
Each kidney is held in place by connective tissue, called renal fascia, and is surrounded by a thick layer of adipose tissue, called perirenal fat, which helps to protect it. A tough, fibrous, connective tissue renal capsule closely envelopes each kidney and provides support for the soft tissue that is inside.
Which Term Is Used For The Tip Of A Pyramid In The Kidney
The point of each pyramid, called the papilla, projects into a calyx. The surface of the papilla has a sievelike appearance because of the many small openings from which urine droplets pass. Each opening represents a tubule called the duct of Bellini, into which collecting tubules within the pyramid converge.
You May Like: Is Caffeine Bad For Your Kidneys
How Are Most Ureters Damaged
The ureter is the least-often injured genitourinary organ, accounting for less than 1% of all urologic traumas secondary to external violence. Ureteral injury occurs more commonly intraoperatively than from external violent trauma . Blunt trauma and stab wounds rarely result in injury to the ureter. Blunt trauma represents 4.1% and SWs 5.2% of all ureteral traumas. The most common ureteral injuries from external violence are from gunshot wounds .
Blood Supply And Lymphatics
The main blood supply to each kidney comes through its respective renal artery. Each renal artery has three critical branches: the inferior adrenal artery, the capsular artery, and the ureteric artery. Additional branches stem from each renal artery as it penetrates the hilum of the kidney, dividing into ventral and dorsal rami and then segmental arteries as they protrude further into the renal parenchyma. Segmental arteries ultimately divide into lobar branches and interlobular arteries. These final arterial segments are critical as the arterioles branching from these segments serve as the afferent arterioles of the glomeruli.
Don’t Miss: What Size Are Kidney Stones
What Is The Function Of The Peritubular Capillaries
Peritubular capillaries help your urinary system get rid of waste. They move waste and excess water through your kidneys nephrons . The waste travels into your bladder and leaves your body through urine .
Peritubular capillaries also reabsorb substances your body needs to work properly, such as amino acids, minerals and glucose . They supply blood and oxygen to the cells in a system of tubes in your kidneys as well.
What Is The Likelihood Of Subsequent Hypertension
Documented posttraumatic hypertension occurs in < 2% of patients and is rennin mediated. Onset generally occurs within the first several months of injury. The mechanisms of posttraumatic hypertension may be the result of renal artery stenosis or occlusion, renal parenchymal compression , and posttrauma arteriovenous fistula.
Key Points: Principles of Ureteral Repair
- 1
Any level of primary ureteral anastomosis should be performed maintaining adequate ureteral vascular supply during dissection of ureteral ends, tension-free ureteral anastomotic site, over stent with absorbable suture.
- 2
-
For a distal injury in the lower third ureter below the iliac vessels, ureteroneocystostomy is recommended. If more ureteral length is needed to keep the anastomosis tension free, a Bohari Flap and Psoas Hitch may be performed.
- 3
-
For middle and proximal third injuries, end-to-end anastomosis is recommended, but anastomosis stricture rate is higher than the proximal or distal ureteral repair.
- 4
-
For a proximal injury , more common in children, immediate laparotomy and surgical repair is needed.
You May Like: What Age Can You Get Kidney Stones
What Is The Likelihood Of Subsequent Hypertension In Patients With Renal Trauma
Posttraumatic hypertension can occur in < 2% of renal trauma patients. The onset usually occurs in the first several months of the trauma. The mechanism of posttraumatic hypertension is renin mediated and can be a result of renal artery stenosis or occlusion, renal parenchyma compression, and posttraumatic arteriovenous fistula. Acute hypertension may occur in cases of âPage kidneyâ due to large retroperitoneal hematoma with or without urine leak that compresses the kidney.
Pearls And Other Issues
Ureteral injuries are rare, but a high level of suspicion for these injuries is necessary when performing an operation with high risk for ureteral injury because immediate identification of the injury is the most important prognostic factor. If a ureteral injury is suspected, an RPG can be obtained at the time of the procedure. Another method to identify the injury involves direct inspection of the ureters using intravenous dyes such as methylene blue and indigo carmine to evaluate for dye leakage along the course of the ureter. Injury treatment will vary on the location and extent of the injury. Treatment can be as simple as ureteral stent placement and as complicated as using a portion of ileum as ureter replacement.
Also Check: How Much Is A Kidney Worth In Usa