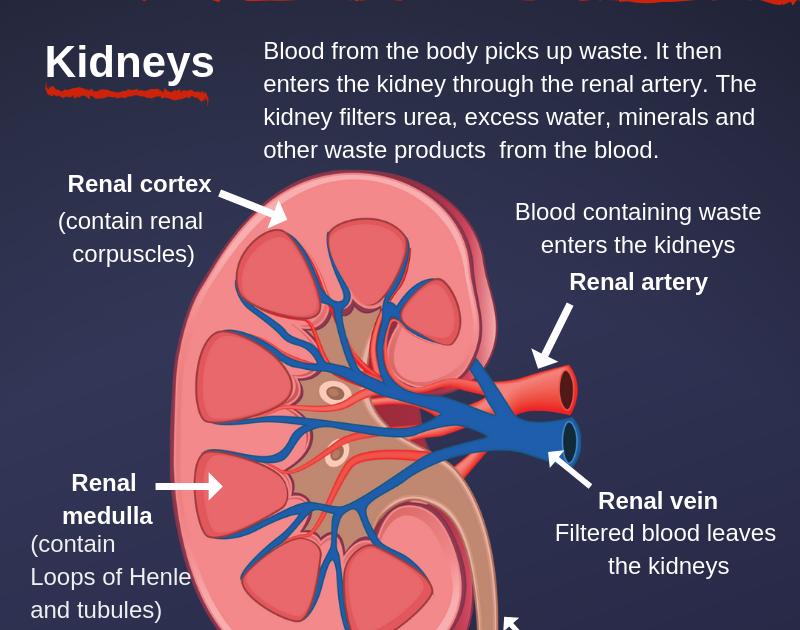
How Do My Kidneys Work
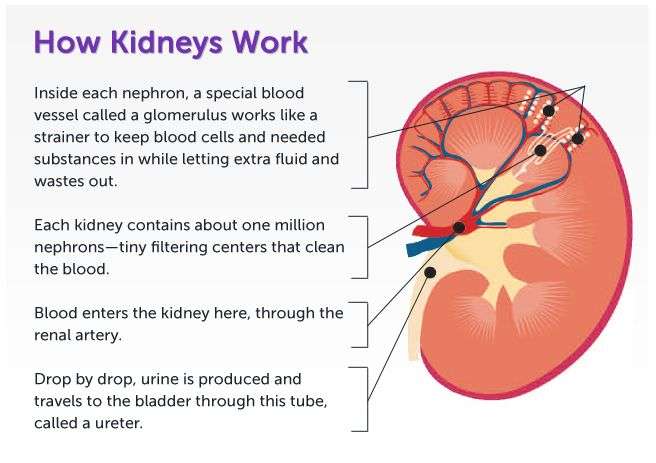
Each of your kidneys is made up of about a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron includes a filter, called the glomerulus, and a tubule. The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes.
Normal Physiology Of Kidney
Filtration is a key kidney function and is the first step that occurs in the kidneys for the purpose of removing various substances from the blood that will ultimately be eliminated from the body .
Filtration involves the passage of certain fluid portions of the blood out of the glomerular capillaries through pores and into the glomerular capsule solids such as red blood cells and large proteins are not permitted to cross the capillary barrier.
You must know What causes low levels of Sodium??
The resulting glomerular filtrate is composed mostly of water with some solutes. Solutes that are freely filterable include glucose, creatinine, uric acid urea, and electrolytes. The main driving force for this filtration is the pressure of the blood within the glomerular capillaries that arises from the blood pressure in the general circulation.
Anything that affects the filtration pressure alters the glomerular filtration rate , which is the rate at which water and molecules cross the glomerular capillary membrane. Constriction of the afferent arterioles would decrease filtration pressure and thus decrease the GFR.
On the other hand, constriction of the efferent arterioles increases the filtration pressure and tends to increase the GFR. Alternatively, cardiovascular disorders such as heart failure, where the heart doesnt pump effectively to maintain the normal circulation of the blood, may also lead to a reduction in GFR.
What Does The Test Measure
The test provides a calculation of the glomerular filtration rate, which reflects how well the kidneys are filtering the blood and is represented in milliliters per minute . The result is often listed as milliliters per minute per 1.73 square meters of body surface area .
In an eGFR test, this rate is not measured directly. Instead, it is estimated by measuring another substance in the blood. Most often, creatinine is measured, and then special formulas calculate eGFR based on the level of creatinine in the blood.
Creatinine is naturally produced as a result of the bodys process of supplying energy to muscles. The kidneys filter and remove creatinine from the blood. Typically the amount of creatinine generated is relatively constant, so changes in creatinine levels in the blood can be an indicator of abnormal kidney function.
Not everyone produces the same amount of creatinine, though, which is why eGFR calculators can include factors such as age, sex, height, and ethnicity along with your creatinine levels in order to estimate the glomerular filtration rate.
While commonly used, creatinine is not the only substance that can be used to estimate GFR. For example, some eGFR tests measure cystatin C, which is a protein made by many types of cells in the body. The effects of individual factors, such as muscle mass and diet, are different when calculating eGFR using cystatin C, so this method of eGFR testing may be more accurate in some circumstances.
Read Also: Braggs Apple Cider Vinegar For Kidney Stones
The 7 Functions Of The Kidneys
Most people know that the primary function of the kidneys is to eliminate waste products from the body by flushing them out with urine. However, did you know that there are at least 6 other fabulous functions you should thank your kidneys for?
Shaheen Motiwala, MD is one of our nephrologist at Florida Kidney Physicians who loves to educate patients. Here is a brief overview of the 7 primary functions of the kidneys to help patients become more familiar with how these amazing organs work.
Nerve Supply Of Kidney
- Kidney and nervous system communicates via renal plexus .
- Renal nerve arise from superior mesenteric ganglion and enter the hilum of each kidney and follow branches of renal artery to reach individual nephrons.
- These nerves consist mostly of sympathetic fibers that trigger vasoconstriction in kidney.
- Sensory input from the kidney travels to the T10 -11 levels of spinal cord and is sensed in the corresponding dermatome. thus, pain in the flank region may be referred from corresponding kidney.
Recommended Reading: What Laxative Is Safe For Kidneys
Components Of Kidney Function Test
The components of the Kidney function test could be broadly divided into two categories.
The tests that are part of the Kidney Function test panel are:
- Urine examination
- Dilution Test
Urine Examination
This examination consists of a physical examination where the color, odor, quantity, specific gravity etc of the urine is noted. Microscopic examination of urine is done to weed out any pus cells, red blood cells casts, Crystals etc.
Serum Urea
Urea is the end product of the protein catabolism. The urea is produced from the amino group of the amino acids and is produced in the liver by means of the Urea cycle. Urea undergoes filtrations at the glomerulus as well as secretion and reabsorption at the tubular level. The rise in the level of serum urea is generally seen as a marker of renal dysfunction especially glomerular dysfunction. Urea level only rises when the glomerular function is reduced below 50%. The normal serum urea level is between 20-45 mg/dl. But the level might also be affected by diet as well as certain non-kidney related disorders. A high protein diet might increase the blood urea level. Similarly, a low protein diet might decrease blood urea level.
Blood Urea Nitrogen
Calcium
Normal Results: 8.5 to 10.2 mg/dlC
Serum Creatinine Level
Dilution Test
Stay tuned with BYJUS to know more in detail about the kidney, kidney function test and importance of excretory system.
Normal Kidney Size Of Adults
When fully developed, the kidneys are roughly the size of a fist.
In more precise measurements, the average size of an adult human kidney is about 10 to 13 cm long, approximately 5 to 7.5 cm wide and about 2 to 2.5 cm thick.
On average, a kidney weighs approximately 150 to 160 grams and, together, both kidneys weigh about 0.5 percent of total body weight. Usually, the left kidney is slightly larger than the right.
These measurements and weights represent the typical ranges of a healthy, adult human kidney.
Actual kidney size is directly correlated with, height, age and BMI . Therefore, taller people with greater BMI tend to have larger kidney dimensions than shorter persons with less BMI. Also, as people age, there is a tendency for their kidneys to shrink a bit.
Renadyl All-Natural Probiotic Supplement for Kidney Health, Kidney Support, Kidney Cleanse, Kidney Restore – Vegetarian, Non-GMO, Sugar-Free
THE WORLDS FIRST AND ONLY PROBIOTIC FOR KIDNEY FUNCTION: Renadyl is formulated with all-natural strains of specific beneficial bacteria that have an affinity for uremic toxins like urea, creatinine, uric acid, and several other nitrogenous waste products*. Kidneys that dont function properly are unable to filter the uremic and nitrogenous toxins.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Don’t Miss: Chocolate And Kidney Stones
Kidney Gfr Chart By Age And Ckd Stages Table
Synopsis: Chart of Kidney Glomerular Filtration Rate number according to your age, includes table showing chronic kidney disease stages. Your GFR number tells you how much kidney function you have, as kidney disease gets worse, the GFR number goes down. “Normal” GFR is approximately 100 but you will often see it reported as > 90 or > 60 . The normal range of Kidney Glomerular Filtration Rate is 100 to 130 mL/min/1.73m2 in men and 90 to 120mL/min/1.73m2 in women below the age of 40.
What Is Kidney Disease
In simple terms, kidney disease means your kidneys have become damaged and can no longer perform their key functions properly. Its a serious condition and its important to receive immediate medical care.
There are two forms of kidney disease:
-
Acute kidney disease is known to occur pretty suddenly and over a short period of time, its sometimes referred to as acute kidney injury.
-
Chronic kidney disease is a long-term condition which can get worse over time, sometimes developing into chronic kidney failure,
Read Also: Carbonated Water And Kidney Stones
Can Kidney Disease Be Treated
Kidney disease can be treated successfully. Patients are usually evaluated by the nephrologist and a set of blood and urine tests are ordered. They also frequently have renal ultrasound ordered to assess kidney size. Occasionally renal biopsy might be needed when a small kidney sample is obtained using a tiny needle. That helps to make a final diagnosis and estimate prognosis and chance of recovery. The first step in the treatment of CKD is to determine the underlying cause. Multiple medications are available to treat kidney disease and the selection of treatment is frequently based on biopsy results. When treatment is not successful or kidneys are damaged before treatment is started some patients might require dialysis.
Acute kidney injury is a sudden inability of the kidneys to perform their function. This can result in accumulation of excess fluids, salts, and waste in the body. This condition can develop quickly over the course of a few hours or days. AKI typically occurs due to an injury, illness or as a side effect of certain medications. AKI can occur in a patient with normal kidney function or in someone who already has chronic kidney disease. Treatment of acute kidney injury can frequently results in improvement of renal function but can also be irreversible leading to residual renal damage.
Functional Structure Of The Kidneys
nephrons
1. The tubule begins with a hollow enlargement called Bowman’s capsule, which is where water and solutes initially enter the tubule from the bloodstream. This process is known as filtration. The structure comprised of Bowman’s capsule and associated capillaries is called the renal corpuscle.
2. From Bowman’s capsule the tubular fluid flows towards the proximal tubule, which remains in the outer layer of the kidney. The proximal tubule is the major site of reabsorption of water and solutes in equal proportions from the filtered tubular fluid.
3. Then the tubule dips into the hairpin loop of Henle, which descends toward the center of the kidney and then rises back to the cortex. The loop of Henle is also a major site of reabsorption, but unlike the proximal tubule, proportionately more solute than water is reabsorbed, so the tubular fluid is dilute relative to plasma by the end of this segment.
4. The next segment is the distal tubule, which like the proximal tubule remains in the cortex. Both reabsorption and secretion take place in this segment, which is where sodium and potassium concentrations and the pH of the tubular fluid are adjusted to ensure homeostasis.
1. An afferent arteriole takes blood to the renal corpuscle, where the blood passes through the first capillary bed, a ball-shape tuft known as the glomerulus.
2. An efferent arteriole takes blood away from the glomerulus.
Recommended Reading: Does Carbonated Water Cause Kidney Stones
Stages Of Kidney Disease In Children And Adults Ages 2+
Stage 1
Kidney damage with normal or increased GFR
eGFR 90 or above and other signs of kidney damage present
Stage 2
Kidney damage with mild decrease GFR
eGFR 60-89 and other signs of kidney damage present
Stage 3a
Mild to moderate decrease GFR
eGFR 45-59
Moderate to severe decrease GFR
eGFR 45-59
Stage 5
Four Key Concepts And Talking Points
1. Talk to patients about their kidneys, CKD, and their risk.
What is CKD? CKD means the kidneys are damaged and may no longer filter blood well. This damage happens over many years. As more damage occurs, the kidneys are unable to keep the body healthy – then dialysis or a kidney transplant may be needed to maintain health.
How can I lower my risk for CKD? The steps you take to manage your diabetes and high blood pressure also help protect your kidneys. Choosing healthy foods, quitting smoking, and being more physically active are all important steps.
2. Communicate the importance of testing and how CKD is diagnosed.
What are the symptoms of CKD? Most people with CKD have no symptoms until their kidneys are about to fail. The only way to know if you have kidney disease is to get tested. The sooner kidney disease is found, the sooner you can take steps to begin treatment and keep your kidneys healthier longer.
How do you check for CKD? A blood test and a urine test are used to find kidney disease. Because you are at risk, you should get these tests regularly:
- GFR – A blood test measures how much blood your kidneys filter each minute, which is known as your glomerular filtration rate .
- Urine Albumin – A urine test checks for albumin in your urine. Albumin is a protein that can pass into the urine when the filters in the kidneys are damaged.
3. Explain the progressive nature of CKD and the basics of treatment.
4. Begin to speak about dialysis and transplantation.
Read Also: What Is The Va Disability Rating For Kidney Disease
Kidney And Urinary System Parts And Their Functions
-
Two kidneys. This pair of purplish-brown organs is located below the ribs toward the middle of the back. Their function is to:
-
Remove waste products and drugs from the body
-
Balance the body’s fluids
-
Release hormones to regulate blood pressure
-
Control production of red blood cells
The kidneys remove urea from the blood through tiny filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron consists of a ball formed of small blood capillaries, called a glomerulus, and a small tube called a renal tubule. Urea, together with water and other waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney.
Two sphincter muscles. These circular muscles help keep urine from leaking by closing tightly like a rubber band around the opening of the bladder.
Nerves in the bladder. The nerves alert a person when it is time to urinate, or empty the bladder.
Urethra. This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
Minimum Advisory Gfr Thresholds For Living Kidney Donation
The evaluation of prospective living kidney donors aims to identify those whom donation would put at an unacceptably high risk of long-term complications, including ESRD. Previous studies have suggested that the risk of ESRD after living kidney donation is not higher than in the general population , but there is a small absolute increased risk . A recent meta-analysis found the relative risk for ESRD was about 9-fold higher in donors compared to non-donors, but the estimated incidence rate was less than 1 case per 1000 person-years . Assessment of GFR in prospective kidney donors is an important factor in determining risk and living kidney donation guidelines have provided threshold GFRs above which the increased risk may generally be considered acceptable. For example, the 2017 KDIGO guideline suggests that a GFR 90 mL/min/1.73m2 is acceptable for donation, while a GFR < 60 mL/min/1.73m2 is not acceptable for donation and a GFR 6089 mL/min/1.73m2 may be acceptable depending on other risk factors .
In our study population of 2974 prospective donors, these GFR thresholds would lead to the exclusion of an additional 5.0% of prospective donors compared to the thresholds in the previous BTS living kidney donation guidelines if adhered to rigidly .
Recommended Reading: What Causes Enlarged Kidney
Stage 3a & 3b Kidney Disease
Moderate decrease in GFR
GFR LEVEL: 30 TO 59 mL/min
Stage 3 CKD, a moderate decrease in kidney function, is divided into 3A and 3B . The following can occur when someone is in stage 3 of CKD:
- Waste products build up in the blood.
- Symptoms include fatigue, too much fluid, urination changes, sleep problems and kidney pain.
- You can often manage stage 3 by changing to a kidney-friendly diet plan as well as managing high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Visit your doctor or nephrologist to help manage kidney disease through kidney-friendly living habits and possibly with prescription medication.
Also Check: Watermelon And Ckd
Living With One Functioning Kidney
Our kidneys perform many functions that are vital to good health, but it is not unusual to have only one kidney to do the work of two.
- Many people are born with a single kidney.
- Some people have to have one kidney surgically removed because they may have developed an obstruction or a tumour or sustained a severe traumatic injury after an accident.
- Some people may have received a kidney from a living or deceased donor , after their own kidneys have failed.
- Others may have donated one of their kidneys to a loved one or another person with kidney failure .
You May Like: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Your Liver And Kidneys
You May Like: What Laxative Is Safe For Kidneys
What Clinical Trials Are Open
Clinical trials that are currently open and are recruiting can be viewed at www.ClinicalTrials.gov.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
What Is The Normal Range Of Kidney Function
Normalurealevelkidney functionUreakidney function
. Similarly one may ask, what is a good number for your kidneys?
The lower your GFR, the lower your kidney function. A GFR between 130 and 90 is considered normal for most people, but that can vary depending on a person’s body size and race.
what is normal GFR for age? In adults, the normal GFR number is 90 or higher. Having a GFR between 60 and 89 may be normal for some people, including those over age 60. GFR tends to decline as we age even in people without kidney disease.
Also Know, what is normal kidney function percentage?
Completely healthy kidney function is measured at a glomerular filtration rate of around 100, which means that the kidneys are working at 100 percent. Your kidney function is still considered normal if the GFR number is 90 or greater.
Is creatinine level 1.7 Dangerous?
When kidneys are not working well, creatinine builds up in the blood. One formula for estimating kidney function equates a creatinine level of 1.7 mg/dL for most men and 1.4 mg/dL for most women to 50 percent of normal kidney function.
Recommended Reading: Watermelon For Kidneys