What Do The Kidneys Do
Your kidneys have many important functions. They clean toxins and waste out of your blood. Common waste products include nitrogen waste , muscle waste and acids. They help your body remove these substances. Your kidneys filter about half a cup of blood every minute.
In the process:
The kidneys also:
- Control the acid-base balance of your blood.
- Make sugar if your blood doesnt have enough sugar.
- Make a protein called renin that increases blood pressure.
- Produce the hormones calcitriol and erythropoietin. Calcitriol is a form of vitamin D that helps your body absorb calcium. Erythropoietin helps your body make red blood cells.
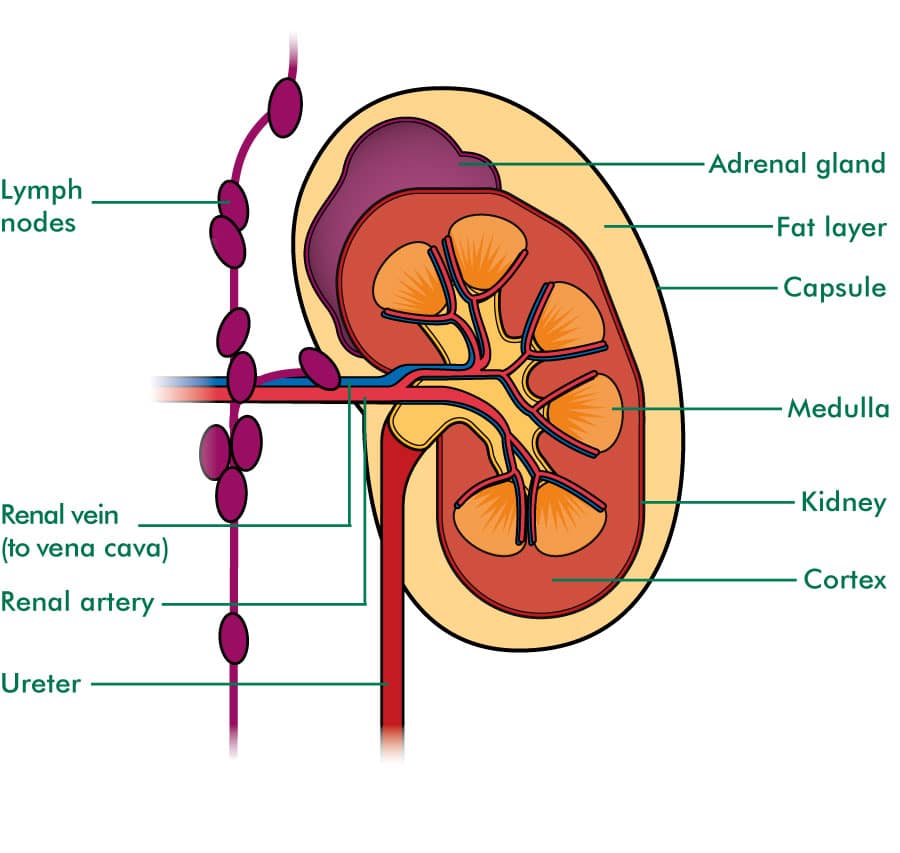
An adrenal gland sits on top of each kidney. It produces hormones, including cortisol, which helps your body respond to stress.
Cortisol also plays a role in:
Where Is The Part Of Kidney
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs on either side of your spine, below your ribs and behind your belly. Each kidney is about 4 or 5 inches long, roughly the size of a large fist. The kidneys job is to filter your blood.
What is inside the kidney?
Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex. The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.
What is the internal anatomy of the kidney?
Kidney Anatomy Internal. The kidney is composed of an inner medulla and an outer cortex surrounded by a tough fibrous capsule. The medulla is composed of a series of conical masses called the renal pyramids. The apex of these pyramids form a papilla which projects into the lumen of the minor calyces.
How Can I Keep My Kidneys Healthy
Its important to have regular checkups and blood and urine tests to measure your kidneys health. You can reduce your risk of developing a kidney problem by:
- Avoiding or quitting smoking and using tobacco products. Your provider can help you find ways to quit.
- Cutting out excess salt, which can affect the balance of minerals in your blood.
- Increasing daily exercise, which can reduce high blood pressure.
- Limiting your use of NSAIDs. NSAIDs can cause kidney damage if you take them too much.
- Watching your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Does Ejaculation Help Pass A Kidney Stone
Structural Explanation Of Kidney Diagram
Excretion is a crucial part of an organisms life processes. The ingested food is assimilated and the byproducts are eliminated from the system to keep the physiological systems free from toxicity. In humans, kidneys are the prime organs that filter the blood and extract byproducts of metabolism to keep it clean. Here, we will study the different aspects and features of the kidney diagram and understand its functioning.
What Are The Outer And Inner Regions Of The Kidney Called
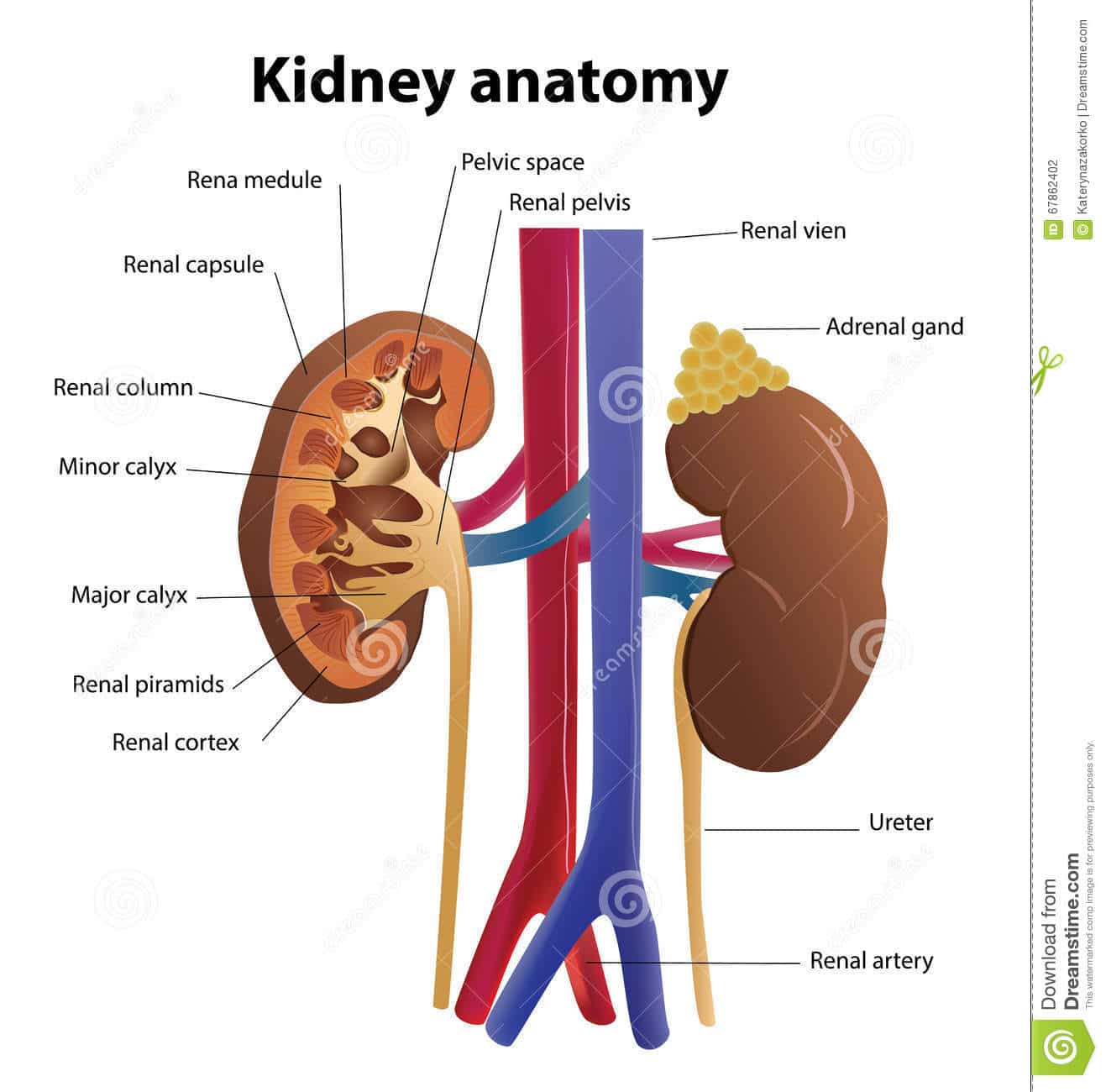
The kidneys are highly vascular and are divided into three main regions: the renal cortex , renal medulla , and renal pelvis (inner region which receives urine through the
What are the two main parts of the kidney?
The functional substance, or parenchyma, of the kidney is divided into two major structures: the outer renal cortex and the inner renal medulla. Grossly, these structures take the shape of eight to 18 cone-shaped renal lobes, each containing renal cortex surrounding a portion of medulla called a renal pyramid.
What are parts of kidney?
The Kidneys Are Composed of Three Main Sections Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex.
Recommended Reading: What Blood Vessel Takes Blood To The Kidney
Tubular Reabsorption And Secretion
Tubular reabsorption occurs in the PCT part of the renal tubule. Almost all nutrients are reabsorbed, and this occurs either by passive or active transport. Reabsorption of water and some key electrolytes are regulated and can be influenced by hormones. Sodium is the most abundant ion and most of it is reabsorbed by active transport and then transported to the peritubular capillaries. Because Na+ is actively transported out of the tubule, water follows it to even out the osmotic pressure. Water is also independently reabsorbed into the peritubular capillaries due to the presence of aquaporins, or water channels, in the PCT. This occurs due to the low blood pressure and high osmotic pressure in the peritubular capillaries. However, every solute has a transport maximum and the excess is not reabsorbed.
In the loop of Henle, the permeability of the membrane changes. The descending limb is permeable to water, not solutes the opposite is true for the ascending limb. Additionally, the loop of Henle invades the renal medulla, which is naturally high in salt concentration and tends to absorb water from the renal tubule and concentrate the filtrate. The osmotic gradient increases as it moves deeper into the medulla. Because two sides of the loop of Henle perform opposing functions, as illustrated in Figure 22.8, it acts as a countercurrent multiplier. The vasa recta around it acts as the countercurrent exchanger.
How Do My Kidneys Filter Blood
Each kidney contains more than a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron consists of:
- Glomeruli: Glomeruli are groups of tiny blood vessels that perform the first stage of filtering your blood. They then pass filtered substances to the renal tubules. The name for this process is glomerular filtration.
- Renal tubules: These tiny tubes reabsorb and return water, nutrients and minerals your body needs . The tubules remove waste, including excess acid and fluids through a process called diffusion. Your body sends the remaining waste through your kidneys collecting chambers. Eventually, it leaves your body as pee.
You May Like: Can Kidney Stones Make You Tired
What Are The Three Primary Structures Of The Kidney
It is possible to divide the kidneys into three sections.
Each kidney is made up of three parts: an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex, which is located in the kidney.
What is the shape of the kidney?
The kidneys are comprised of two bean-shaped organs that are each about the size of a fist.
What colour does the kidney appear to be?
In appearance, they resemble a bean, and their colour is reddish-brown. Each kidney is roughly the size of a fist clenched in the palm of your hand.
What are the structure and function of the kidneys?
The kidney contains a structural filtration unit known as a nephron, which filters the blood as it passes through it. Each kidney contains a million nephrons, which are tiny blood vessels. During this process, essential substances such as glucose, amino acids, salts, and the necessary amount of water are reabsorbed before the blood is returned to circulation.
In what way do the kidneys serve a purpose?
Their primary function is the removal of toxins from the bloodstream and the conversion of waste products into the urine, respectively. It is estimated that each kidney weighs 160 grammes and that it excretes one to one and a half litres of urine each day. Approximately 200 litres of fluid enters the bloodstream every 24 hours through the two kidneys.
What are the structures that surround the kidney and protect it?
Functions Of The Kidney
An increase in urine concentration.
Increase in the water reabsorption.
There is a reopening of the portion of the collecting duct, which allows the water back into the body.
The urea in the medulla of the kidney is retained back rather than it getting excreted, as it draws in water.
-
Blood Pressure Regulation: When it is required, the kidneys help in regulating the blood pressure of the body, they are also responsible for the slower adjustments. The kidneys help in adjusting the long-term pressure in the arteries by causing changes in the fluid outside of cells. The medical term of the fluid is extracellular fluid. The changes in the extracellular fluid occur after the release of a vasoconstrictor called angiotensin II. The blood vessels get narrowed only because of the hormone vasoconstrictors. These hormones also work with other functions to increase the kidneys absorption of sodium chloride or salt. When there is an absorption of the salt, this effectively increases the size of the extracellular fluid compartment and raises blood pressure. Consumption of excessive alcohol, smoking, or obesity can alter the blood pressure which can lead to damage of the kidneys.
-
Secretion of Hormones and Active Compounds: The kidneys are responsible for the release of many active compounds such as Renin, erythropoietin, and calcitriol.
-
Below a diagram that shows a mammal kidney slide is given
Don’t Miss: Is Kidney Dialysis Covered By Medicare
Structure Of Kidneys With Diagram
These organs have an inner concave space where many smaller structural units are stacked. The blood vessels connect and enter these organs through a small notch present at the inner concave portion called the hilum. In fact, the ureter also emerges from this notch and enters the urinary bladder.
The Different Parts of a Kidney are as Follows.
-
Capsule: As per the structure of kidney diagram, the outermost layer of this organ is called a capsule. Inside the kidney, two prominent zones are found. The outer zone is called the cortex and the inner one is called the medulla. The former part that is the cortex extends and forms the columns of Bertin amidst the medullary pyramids.
-
Ureter: It extends from the renal pelvis of each kidney. Its prime function is to carry and deposit urine in the urinary bladder. If you look at the kidney diagram labeled closely, you will understand how this thin urine pipe emerges from each kidney.
To summarize the structure of kidney diagram, the renal cortex comprises the outer part of this organ where the Malpighian corpuscles and the convoluted tubules of the nephrons exist. It is surrounded by fatty tissue at the outer portion for shock absorption and protection.
Is It Kidney Pain Or Back Pain
Kidney pain and back pain are similar, and people often confuse them.
Back pain usually occurs in your lower back.
Kidney pain is deeper in your body and higher up your back. Youll likely feel pain in your sides or your middle- to upper-back area . The pain may progress to other areas, including your abdomen or groin.
Kidney pain results from swelling or blockage of your kidneys or urinary tract. Symptoms include fever, nausea, vomiting or pain when you pee.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When One Kidney Stops Working
What Is The Function Of Kidneys In Our Body
Why are the kidneys important? Your kidneys remove wastes and extra fluid from your body. Your kidneys also remove acid that is produced by the cells of your body and maintain a healthy balance of water, salts, and mineralssuch as sodium, calcium, phosphorus, and potassiumin your blood.
What is the external structure of the kidney?
External structure: Each kidney is reddish-brown, bean shaped organ and is about 4 inches long and 2 inches wide. It has a medial concave surface and a lateral convex surface. On the medial concave border of each kidney, there is a vertical slit called hilum, which is bounded by thick lips of the renal substance.
What are the parts of the kidney and their functions?
The kidney is a critical organ in the bodys renal system. Some of the larger components in the anatomy of the kidney include the renal pelvis, renal medulla, and renal cortext. Kidneys aid in filtering toxins and maintaining fluid balance. In addition to these functions, the kidneys play other important roles in maintaining health.
Passive Reabsorption Of Water
With the active absorption of sodium and chloride, water reabsorption occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule for the body. Water is reabsorbed in Henleyâs loop and distal convoluted tubule. Water reabsorption occurs in the distal convoluted tubule mainly under the influence of the ADH hormone. Thus, after filtration and reabsorption, thick urine with secretion substances are formed .
Read Also: How To Identify Kidney Pain
The Structure And Function Of The Kidneys
Angela Underwood’s extensive local, state, and federal healthcare and environmental news coverage includes 911 first-responder compensation policy to the Ciba-Geigy water contamination case in Toms River, NJ. Her additional health-related coverage includes death and dying, skin care, and autism spectrum disorder.
It is hard to understand the signs and symptoms of kidney disease unless we appreciate the kidneys role in our body. This article explains what the kidneys do and how they accomplish their function.
The Internal Structure Of Kidney
Renal cortex: It is the dark red part on the outside of each human kidney when it is bifurcated vertically is called the renal cortex.
Renal medulla: The light red part on the inside the kidney is called the renal medulla. About 1 million nephrons are present in the cortex and medulla of each kidney.
Renal pelvis: The funnel-shaped part of the ureters that connect to the concave part of the hilum of the kidney is called the renal pelvis.
Renal pyramid: Parts of the cortex are enlarged in places of the medullary part of the kidney. The enlarged parts of the cortex divide the medulla into several triangular parts, called the renal pyramid.
- Few renal pyramids form Renal papilla.
- Few renal papillae connected to form Minor calyx.
- Minor calyx combined to form Major calyx.
Renal pelvis is divided into two or three major calyces and four minor calyces. The ureter from the renal pelvis carries the urine from the kidneys directly to the bladder & .
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Kidney Disease
What The Kidneys Do
Your kidneys are silent workhorses, toiling 24/7 to clean your blood of impurities and toxins that build up from the body’s metabolism. This waste fluid, which we know better as urine, is then excreted. However, the kidneys role extends to well beyond just making urine. They are your bodys very own laboratories that test your blood continuously to make sure every electrolytes concentration is within the specific range that is necessary for your body to function.
As an example, lets consider an electrolyte in your blood, like potassium. Potassium is an electrolyte whose concentration needs to be within a tight range for your heart to generate its normal electric impulses. These impulses cause the heart to beat at a set rhythm or pulse. Both high or low potassium can interfere with this electricity generation and cause your heart to go into an abnormal rhythm. This abnormal rhythm, called arrhythmia, is life-threatening and could cause a person to drop dead in a matter of seconds. However, this does not happen in normal circumstances, because the moment the kidneys detect a rise in the bloods potassium concentration, they dump the extra potassium into urine, thus keeping the potassium level constant in the blood. If it weren’t for your kidneys, a typical meal that you eat could turn out to be a life-endangering experience owing to its potassium content.
Here are some other functions the kidneys serve:
Excretion Of Urine Out Of The Body
The urine produced in the nephron enters the minor calyx through the Bellini duct, being accepted by the collecting tubule. The urine comes from the minor calyx to the major calyx and eventually reaches the ureters. Urine from the ureters is temporarily stored in the bladder and is excreted out of the body through the urethra .
Also Check: Is Protein Harmful For Kidney
Kidney Structures And Functions Explained
Your kidneys are paired organs found on each side of the back portion of the abdominal cavity. The larger left kidney is located a bit higher than the right kidney. Unlike other organs found in the abdomen, the kidneys are located behind the lining of the abdominal cavity, thus they are considered retroperitoneal organs. These bean-shaped organs are protected by the back muscles and the ribs, as well as the fat that surrounds them like a protective padding. Learn more about the kidney structures and functions from this short article.
Clinical Relevance: Variation In Arterial Supply To The Kidney
The kidneys present a great variety in arterial supply these variations may be explained by the ascending course of the kidney in the retroperitoneal space, from the original embryological site of formation to the final destination . During this course, the kidneys are supplied by consecutive branches of the iliac vessels and the aorta.
Usually the lower branches become atrophic and vanish while new, higher ones supply the kidney during its ascent. Accessory arteries are common . An accessory artery is any supernumerary artery that reaches the kidney. If a supernumerary artery does not enter the kidney through the hilum, it is called aberrant.
Read Also: What Is 3rd Stage Kidney Failure
Structure Of The Kidney
In this lecture, we are going to learn about on Structure of the Kidney In briefly with a different example.
Table of Content
These two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist, are connected by a tube that runs through the abdomen. Each kidney is surrounded by a tough, fibrous renal capsule, which provides support for the soft tissue that lies within. Additionally, two layers of fat serve as additional protection against the elements. The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys. The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs that are found in vertebrates. It is common for adult humans to have two retroperitoneal spaces, which measure approximately 12 centimetres in length on the left and right sides, respectively. During a day, blood enters through the paired renal arteries and is expelled through the paired renal veins. Each kidney is equipped with a ureter, which is a tube that transports excreted urine to the bladder after each kidney function.
What is the physical structure of the kidney?
Inside, the kidney is divided into three regions: an outer cortex, a medulla in the middle, and the renal pelvis in the hilum of the kidney. The outer cortex is divided into two parts: the cortex and the renal pelvis. Located in the concave part of the bean-shaped kidney, the hilum is the point at which blood vessels and nerves enter and exit, as well as the point at which the ureters exit.