The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus: From Anatomical Peculiarity To Physiological Relevance
In the late 1920s, when Homer Smith started his work on the kidney, renal physiology as a field was not particularly advanced in fact, it was considerably underdeveloped. This is reflected, for example, in the following statements of Alfred Richards, one of the other greats of kidney physiology in that same time:
The literature of investigation of the kidney, since Bowman, contains no great illuminating discoveries comparable to those which are so conspicuous in other fields. Many of the questions of kidney function which are now being actively debated by physiologists are practically identical with those which were subjects of controversy seventy-five years ago. Is the Malpighian body with its contained glomerulus a filter or is it a secretory structure? Is the epithelium which composes the tubule walls capable of secreting substances from blood into lumen of tubule, or is its task that of permitting or enabling restoration to the blood of substances lost to it in passage through the glomerulus? .
In addition to his textbooks, he wrote four other books, Kamongo, or The Lungfish and the Padre , The End of Illusion , Man and His Gods , and From Fish to Philosopher . Particularly pleasant to read is From Fish to Philosopher. His enthusiasm and understanding for comparative physiology has substantial resonance in this era in which we learn more and more about the extent of evolutionary conservation both at the genomic and functional level.
What Is The Significance Of Jga In Kidney Function
What is the significance of Juxtaglomerular apparatus
The juxtaglomerular apparatus is a specialized structure formed by the distal convoluted tubule and the glomerular afferent arteriole. It is located near the vascular pole of the glomerulus and its main function is to regulate blood pressure and the filtration rate of the glomerulus.
One may also ask, what do Juxtaglomerular cells monitor? Urinary System: Juxtaglomerular complexThe afferent arteriole in this region contains specialised secretory cells called juxtaglomerular cells, that secrete renin. These cells do two things: They monitor blood pressure, by measuring how much the arteriole wall is stretched.
Simply so, what is the function of the macula densa cells of the Juxtaglomerular complex?
Macula densa cells in the distal nephron, according to the classic paradigm, are salt sensors that generate paracrine chemical signals in the juxtaglomerular apparatus to control vital kidney functions, including renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and renin release.
What are the three components of the Juxtaglomerular apparatus?
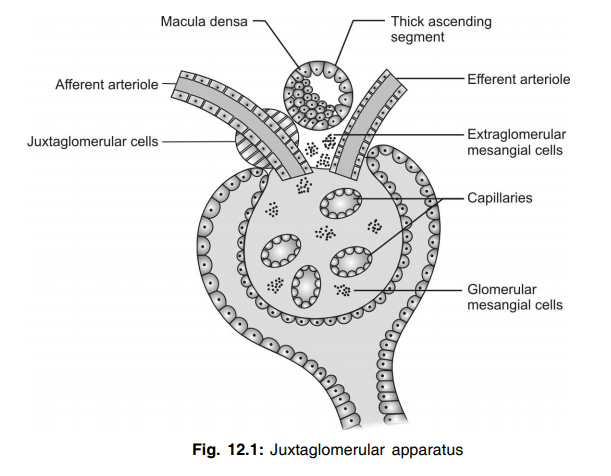
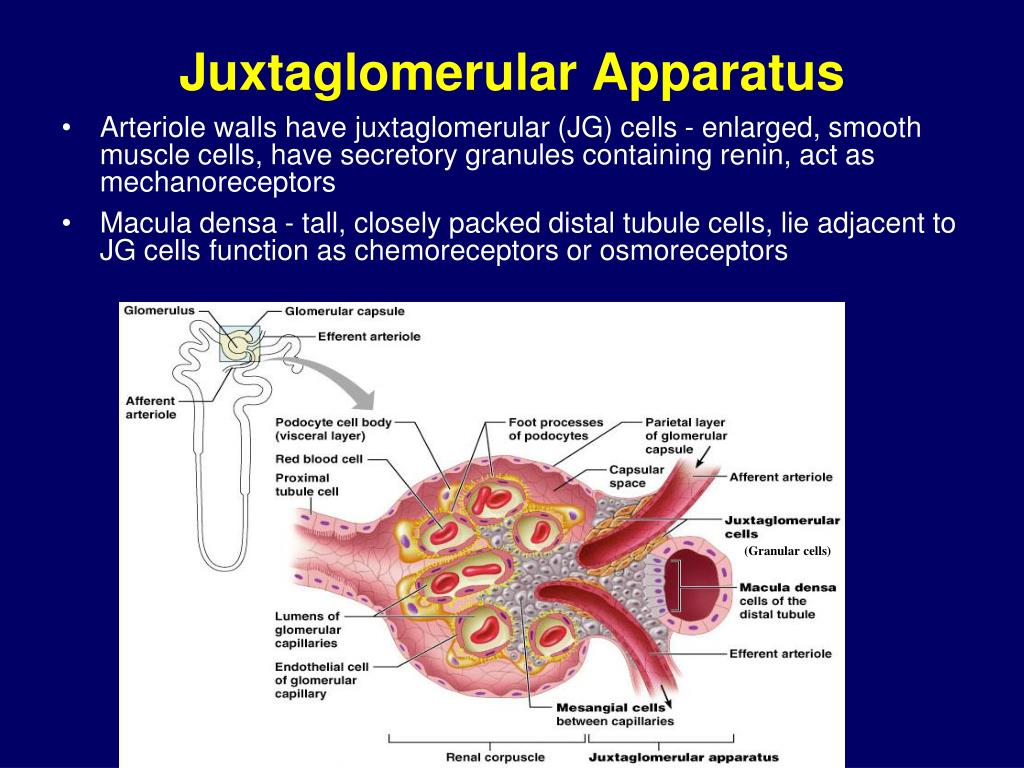
The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of three cell types: the macula densa cells, the juxtaglomerular cells and the extraglomerular mesangial cells.
Characteristics Of Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Figure 2. Relationship between the rate of loop of Henle perfusion and single nephron GFR determined as the product of early proximal tubular flow rate and the tubular fluid to plasma inulin ratio. Data are from Briggs et al. . Relationship between the rate of loop of Henle perfusion and the associated change of stop flow pressure . Data are from Schnermann et al. .
An important characteristic feature of TGF is its tendency to reset by shifting its operational range into a higher or lower flow range and by changing its sensitivity by either decreasing or increasing the slope of the TGF function. This typically occurs when the signal is forced out of operating range for too long. Often, left shifts are situations of increased angiotensin II, states of volume depletion for example, and right shifts are states of reduced angiotensin II and perhaps increased nitric oxide, volume expansion for example.
In summary, the TGF control system describes an inverse and sigmoidal relationship between SNGFR and VLP its operating point is at the function midpoint, its optimal error compensation is around the operating point, it can reset its operational range and its sensitivity to flow perturbations, it has a tendency for stable oscillations at 35 to 50 mHz , it is a single nephron mechanism although TGF-induced smooth muscle activation can spread by electrotonic coupling , and its vascular effect is long-lasting.
Don’t Miss: Pineapple And Kidney Stones
Tubuloglomerular Feedback And Renin Secretion
Figure 12.8. Role of gap junctions in the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
Components of the TGF calcium wave include ATP release from macula densa cells in response to elevations in tubular NaCl and/or flow rate, and paracrine, purinergic calcium signaling. Extracellular ATP-induced elevations in mesangial, vascular smooth muscle , and renin-producing juxtaglomerular cell i are then propagated via gap junctions to distant cells of the afferent arteriole , efferent arteriole , and glomerulus away from the MD region, causing cell contractions. All cell types of the JGA are abundant in gap junctions , except for the cells of the MD. Vascular endothelial cells in the AA, EA, and G are also connected with each other and JGCs and VSMCs via gap junctions, and are involved in the calcium wave of TGF.
24
Tamar S. Polonsky, George L. Bakris, in, 2020
What Is The Significance Of Juxtaglomerular Apparatus In Kidney Function
Juxtaglomerular apparatus is a complex structure made up of a few cells of glomerulus, distal tubule, and afferent and efferent arterioles. It is located in a specialised region of a nephron, wherein the afferent arteriole and the distal convoluted tubule come in direct contact with each other.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus contains specialised cells of the afferent arteriole known as juxtaglomerular cells. These cells contain the enzyme renin that can sense blood pressure. When glomerular blood flow decreases, it activates juxtaglomerular cells to release renin.
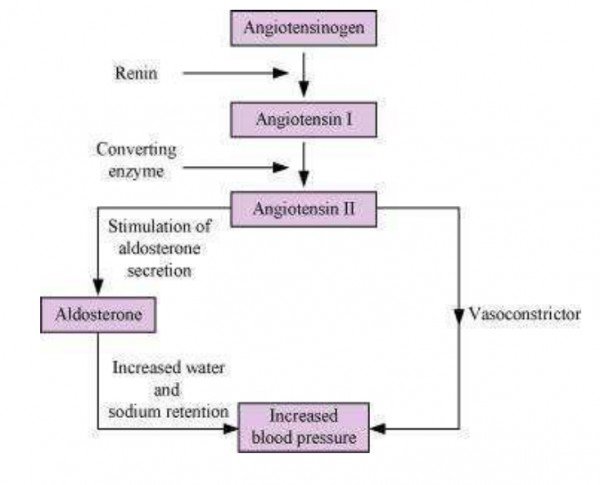
Renin converts the angiotensinogen in blood into angiotensin I and further into angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a powerful vasoconstrictor that increases the glomerular blood pressure and filtration rate. Angiotensin II also stimulates the adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland to produce aldosterone. Aldosterone increases the rate of absorption of sodium ions and water from the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting duct. This also leads to an increase in blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate. This mechanism, known as renin-angiotensin mechanism, ultimately leads to an increased blood pressure.
Also Check: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
What Is The Significance Of Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
-
What is the significance of juxtaglomerular apparatus in kidney function?
August 30, 2011 at 11:12 am#10276Participant
Answer
Juxtaglomerular apparatus is a complex structure made up of a few cells of glomerulus, distal tubule, and afferent and efferent arterioles. It is located in a specialised region of a nephron, wherein the afferent arteriole and the distal convoluted tubule come in direct contact with each other. The juxtaglomerular apparatus contains specialised cells of the afferent arteriole known as juxtaglomerular cells. These cells contain the enzyme renin that can sense blood pressure. When glomerular blood flow decreases, it activates juxtaglomerular cells to release renin.
Renin converts the angiotensinogen in blood into angiotensin I and further into angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a powerful vasoconstrictor that increases the glomerular blood pressure and filtration rate. Angiotensin II also stimulates the adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland to produce aldosterone. Aldosterone increases the rate of absorption of sodium ions and water from the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting duct. This also leads to an increase in blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate. This mechanism, known as renin-angiotensin mechanism, ultimately leads to an increased blood pressure.
Selection Criteria For This Study
In preliminary studies, we found a high frequency of false negative results for JGA T-cell infiltration if tissues with small numbers of glomeruli were included. With less than seven glomeruli or four JGAs in a biopsy only 8.3% of the patients were positive for T-cell infiltration compared to 41.6% when tissues with at least seven glomeruli or four JGAs were studied . Thus, to reduce the risk of false negative results, we used only tissues containing at least seven glomeruli and four JGA areas. Of the 243 NHDN patients that had unstained light microscopy slides available 176 were screened for this study, of whom 89 had adequate numbers of glomeruli or JGA for inclusion. Fourteen of these patients had unclassifiable readings for JGA T-cell infiltration and were not included, leaving 75 patients in this cohort. There were no statistically significant differences in age, age at onset, duration, sex, HbA1c, AER, BP or renal morphometry between this cohort and the other 168 patients in this study. The control subjects were 17 normal kidney donors who were matched for age and sex to the diabetic patients and who underwent a lower pole needle donor kidney renal biopsy at the time of renal transplant surgery.
Table 1 Number of NHDN* patients with and without JGA T-cell infiltration
Also Check: Does Pop Cause Kidney Stones
Function Of Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus or Complex is a specialized region of a nephron where the afferent arteriole and Distal Convoluted Tubule come in direct contact with each other. Juxtaglomeruar Apparatus consists of:
1) Juxtaglomerular cells of afferent arteriole including renin containing and sympathetically innervated granulated cells which function as mechanoreceptors to sense blood pressure.
2) Macula densa cells of Distal Convoluted Tubule which function as chemoreceptors to sense changes in the solute concentration and flow rate of filtrate.
3) Juxtaglomerular/Extraglomerular mesangial cells forming connections via actin and microtubules which allow for selective vasoconstriction/vasodilation of the renal afferent and efferent arterioles with mesangial cell contraction.
Functions of Juxtaglomerlar Apparatus :
Tubuloglomerular Feedback Mechanism
The tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism has 2 components that act together to control GFR:
Increased renal arterial pressure leads to an increased delivery of fluid to the macula densa. The macula densa senses the load and causes constriction of nearby afferent arteriole, increasing the resistance. This will return osmolality and filtrate flow rate to normal.
Norbert Goormaghtighthe Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
In his inaugural paper on the subject , Goormaghtigh described in detail the afibrillar cells of the juxtaglomerular arterioles, principally in an 8-year-old girl who had died of scarlet fever. He characterized them as afibrillar granular cells and identified them with those lining the afferent arteriole described by Ruyter. In addition, he identified a second population of smaller, also afibrillar but agranular, spindle-shaped cells in the vascular pole, and highlighted the rich enervation of the entire area. The second type of cells he described were subsequently termed lacis cells because of their interlacing processes separated by basement membrane. Like Oberling, he mentioned the similarity of his findings to the subcutaneous glomi of Masson . Masson had used the term glomus to describe the subcutaneous plexus of arterio-venous anastomoses rolled upon itself and embedded in fibrous tissue that blends into the surrounding dermis. The analogy made was not only to shape but also the appearance of the cells lining the glomic arterioles and the abundance of neural fibres supplying these neuro-muscular cells described by Masson, hence the title of Goormaghtigh’s first manuscript Les segments neuro-myo-artériel juxtaglomerulaires des reins .
Number of publications per 5-year period listed in PubMed under the search word juxtaglomerular apparatus for the period 19512004.
Also Check: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
What Substance Does The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Secrete To Control Blood Pressure
ReninRenin is an enzyme secreted by the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney. It interacts with aldosterone in a negative-feedback loop. Some hypertensive patients are defined as having low-renin and high-renin essential hypertension. About 20% of hypertensive patients have suppressed plasma renin activity.
Ureters Bladder And Urethra
The ureters originate at the renal hilus and conduct urine from the kidney to the bladder. Anatomically, the ureters consist of an epithelium-lined lumen surrounded by smooth muscle, nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. Peristalsis, originating in the renal calyx, propels urine toward the bladder.
The bladder is a highly distensible organ lying behind the symphysis pubis. The wall of the bladder consists of an epithelial layer, a mesh-like arrangement of smooth muscle layer, and a thin connective layer containing nerves and blood vessels. This anatomic arrangement allows the wall of the bladder to distend to a large volume without generating much tension. Inflow to the bladder comes from the ureters, which connect with the bladder at the ureterovesical junction. Urine passing from the bladder into the urethra must pass through the smooth muscular internal bladder sphincter.
HISTOLOGY
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
The urethra extends from the bladder to the surface of the body. It consists of an epithelium-lined lumen and a smooth muscle layer. Urine exiting the urethra must pass through the muscular external sphincter.
Kanwar Nasir M. Khan, … Carl L. Alden, in, 2013
Read Also: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Your Liver
What Is The Significance Of Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Jga In Kidney Function Class 11
The juxtaglomerular apparatus is known because its next to the glomerulus. Complete answer: Juxtaglomerular apparatus is an apparatus consisting of a couple of cells of the glomerulus, distal tubule, and afferent and efferent arterioles its involved in maintaining the glomerular filtration rate within the kidney.
Why Is The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Important
The juxtaglomerular apparatus functions to maintain blood pressure and to act as a quality control mechanism to ensure proper glomerular flow rate and efficient sodium reabsorption. The urethra extends from the bladder to the surface of the body. It consists of an epithelium-lined lumen and a smooth muscle layer.
Recommended Reading: Pomegranate Juice And Kidney Stones
Why Is Jga Important
Juxtaglomerular apparatus is an apparatus consisting of a couple of cells of the glomerulus, distal tubule, and afferent and efferent arterioles its involved in maintaining the glomerular filtration rate within the kidney. Juxtaglomerular apparatus plays a crucial role within the renin-angiotensin mechanism.
How Does Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Regulate The Kidney Function
The juxtaglomerular apparatus functions to maintain blood pressure and to act as a quality control mechanism to ensure proper glomerular flow rate and efficient sodium reabsorption. The urethra extends from the bladder to the surface of the body. It consists of an epithelium-lined lumen and a smooth muscle layer.
Recommended Reading: Is Wine Bad For Kidney Stones
Which Of These Will Increase Arterial Blood Pressure
Any factor that causes cardiac output to increase, by elevating heart rate or stroke volume or both, will elevate blood pressure and promote blood flow. These factors include sympathetic stimulation, the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine, thyroid hormones, and increased calcium ion levels.
What Are The Kidneys In Charge Of Regulating
The kidneys ensure that the make-up and volume of the fluids in the body is correct. They help control the chemical balance of the blood and regulate the bodys level of sodium, potassium and calcium. The kidneys remove waste products and excess water from the body and so help to regulate blood pressure.
Don’t Miss: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
Norbert Goormaghtighbiography And Scholarship
It is on this background in the state of the medical sciences that Goormaghtigh made his major contributions on the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the period between the two world wars, both of which to some extent influenced and shaped his personal life. Born on 14 February 1890 in the North Sea port city of Ostend, in West Flanders, Goormaghtigh graduated in medicine from the University of Gent in 1913. Drafted into service at the break of the First World War , he served as a surgical pathologist in an English Field Hospital in Hoogstade. It is there that he met and married an English nurse, Mabel Lawrence, in 1917. The Second World War was equally defining in his life, when his favoured son was accused and imprisoned in Daschau in 1943. The following year, the Gestapo incarcerated him also, albeit for only a short period. The toll of WWII on his work and productivity is reflected in the diminishing number of his publications . His subsequent administrative responsibilities as a rector of the University of Gent , during a particularly difficult period in its history, further hampered and practically ended his investigative career. Following a series of progressively severe and incapacitating cardiac attacks beginning in November 1957, he died on 2 January 1960 .
What Would Happen To Your Blood Pressure If Your Kidneys Could Not Regulate The Production Of Renin
Without renin, blood pressure cannot be protected in the face of sodium depletion. Conversely, in the face of salt loss, excess renin production serves only to maintain, not to increase blood pressure. It is in saltreplete humans that renin may be undesirable and contribute both to hypertension and endorgan damage.
Don’t Miss: Wine For Kidney Stones
What Is The Significance Of Juxta Glomerular Apparatus In Kidney Function
Juxtaglomerular apparatus is an apparatus consisting of a few cells of the glomerulus, distal tubule, and afferent and efferent arterioles It is involved in maintaining the glomerular filtration rate in the kidney. JGA is found to be located in a specialised region of a nephron, where the afferent arteriole and the distal convoluted tubule are in direct contact with each other. The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of certain specialised cells of the afferent arteriole. These cells are known as juxtaglomerular cells and they contain the enzyme renin that can sense blood pressure. When there is a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate, the juxtaglomerular cells get activated and release renin which functions to converts the angiotensinogen in the blood into angiotensin I and further into angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a powerful vasoconstrictor that can increase the glomerular filtration rate or glomerular blood pressure. Angiotensin II further stimulates the adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland to produce aldosterone which increases the rate of absorption of sodium ions and water from the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting duct. Later on, it leads to an increase in the blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate. This mechanism is known as the renin-angiotensin mechanism, ultimately leads to increased blood pressure. Juxtaglomerular apparatus plays an important role in the renin-angiotensin mechanism.
What Activates Macula Densa
A decrease in sodium chloride concentration initiates a signal from the macula densa that has two effects: it decreases resistance to blood flow in the afferent arterioles, which raises glomerular hydrostatic pressure and helps return the glomerular filtration rate toward normal, and it increases renin
Also Check: Is Pineapple Good For Kidney Stones