What Are Parasarcoidosis Syndromes
Many sarcoidosis patients experience complications or symptoms that are not directly related to granulomas or fibrosis. These are called parasarcoidosis syndromes and they can have a significant impact on a patients quality of life. The main parasarcoidosis syndromes are fatigue, vitamin d dysregulation, erythema nodosum, small-fiber neuropathy, pain syndromes, depression, and cognitive impairment.
Fatigue
Fatigue affects a large amount of sarcoidosis patients, even when their other symptoms are under control.
Vitamin D Dysregulation
Vitamin D dysregulation is common in sarcoidosis patients. This is a result of the increase in an enzyme that converts the inactive form of vitamin D into the active form. Doctors often misread vitamin D levels in sarcoidosis patients which can lead to hypercalciumia or hypercalciuria.
Erythema Nodosum
Erythema Nodosum is a skin lesion that develops without granuloma formation. Erythema Nodosum occurs in up to 35% of sarcoidosis patients and presents as tender bumps usually on usually on the front of the legs.
Small-Fiber Neuropathy
SFN occurs in up to 25% of sarcoidosis patients and can significantly impair a patients quality of life. SFN has two sub-categories: painful neuropathy and autonomic neuropathy. Painful neuropathy affects the fibers within the skin that sense heat and pain. This can result in pain, numbness, vibrations or electric shock sensations, and dysesthesias.
Pain Syndromes
- Sarcoiliitis
- Immobility
Depression
Does Sarcoidosis Run In Families
While the latest research does appear to indicate a genetic susceptibility to the disease, more research is needed to clearly identify and confirm the genes involved. However, numerous reports have revealed racial/ethnic and family-line occurrences, including the following:
- Irish immigrants in London have a three-fold likelihood of developing sarcoidosis compared with native Londoners.
- Natives of Martinique living in France have an eight-fold higher chance of developing the disease compared with the native French population.
- African-Americans face a 4 to 17 times greater risk of the disease compared with Caucasians.
- Within individual families, the presence of the disease in a first- or second-degree relative increases the risk by nearly five-fold.
Still other types of disease clusters have been identified, including seasonal and occupational clustering. Researchers in Greece, Spain, and Japan have reported a clustering of diagnoses of sarcoidosis in the months of March to May, April to June, and June to July. In the United States, a higher percentage of cases of sarcoidosis have been reported in health care workers, naval aircraft servicemen, and firefighters.
What Can Happen As The Disease Progresses
In many people with sarcoidosis, the disease appears briefly and then disappears without the person even knowing they have the disease. When sarcoidosis seriously affects the ability of the lungs to function normally, patients may require supplemental oxygen to help them breathe.
Twenty percent to 30% of people have some permanent lung damage. For 10% to 30%, sarcoidosis is a chronic condition, with symptom progression despite treatment that has continued for more than two years. In some people, the disease may result in the deterioration of the affected organ.
When the granulomas or fibrosis seriously affect the function of a vital organ — such as the lungs, heart, nervous system, liver, or kidneys — sarcoidosis can be fatal. Death occurs in 1% to 6% of all patients with sarcoidosis and in 5% to 10% of patients with chronic progressive disease. The leading cause of sarcoidosis-related death in the United States is irreversible pulmonary fibrosis.
You May Like: Seltzer Water Kidney Stones
Tests That Help Diagnose Sarcoidosis
Your doctor will order tests to understand your symptoms and to see which organs are affected. Some common tests are:
- Spirometry a simple breathing test that measures how much and how fast you can move air out of your lungs.
- X-rays to check if there are granulomas or other changes in your lungs.
- CT scan an imaging test that takes a picture of your lungs, brain, or other areas of your body to check for changes.
- Electrocardiograph and 24 hour tape tests that record the electrical activity of your heart to see if it is working properly.
- Ultrasound scan of different areas of your body such as liver or spleen.
- Blood tests to check if your liver and kidneys are working properly, and to see if there are changes in your blood.
Your doctor will choose your treatment based on your symptoms.Whether you need treatment and what type of treatment you need depend on your signs and symptoms, which organs are affected, and whether those organs are working well.
Some people with sarcoidosis have no symptoms. Doctors call no symptoms asymptomatic. If you have no symptoms, you probably wont need treatment. You do need to get regular check-ups, to make sure the sarcoidosis isnt getting worse.
If you have mild sarcoidosis, you may not get any treatment. Your granulomas may stop growing or shrink. Your symptoms may disappear on their own after a few years.
Sarcoidosis Signs And Symptoms
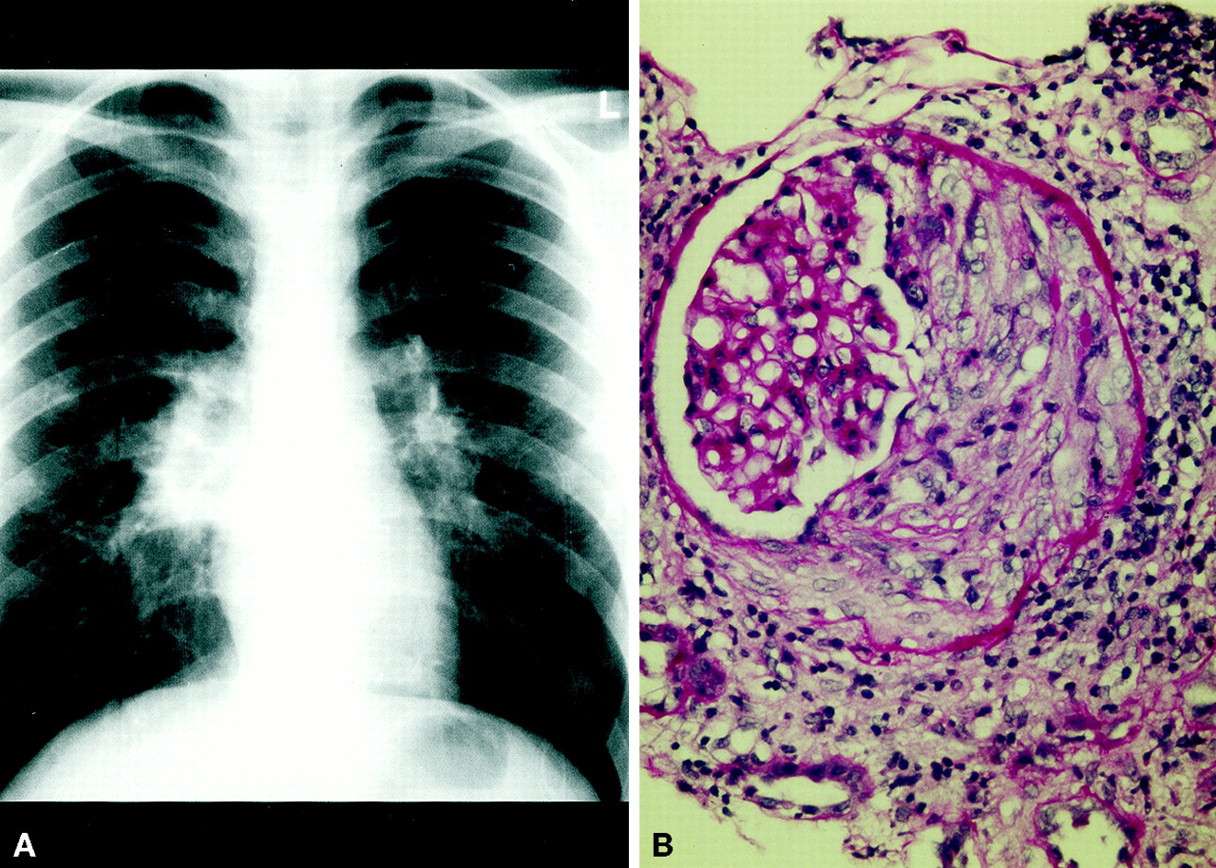
Sarcoidosis symptoms vary widely and may appear to varying degrees and for differing periods of time. Some patients have no symptoms some have symptoms that are unpleasant but not disabling some experience symptoms that disappear with or without treatment then return. If symptoms last for more than two years, the sarcoidosis is considered chronic.
Depending on the part of the body affected, sarcoidosis patients may experience symptoms that include the following:
General symptoms
- Swelling of upper eyelids
Lymph Glands
- Swelling of salivary glands producing a “mumps-like” appearance
Recommended Reading: Is Ginger Good For The Kidneys
Sarcoidosis Risk Factors And Symptoms
It seems like anyone can develop sarcoidosis. To date, only a few risk factors have been isolated. They include age, sex, race and family history . Sarcoidosis occurs between the ages of 20 and 40, most often in women. For some reason, there is a higher rate of the disease among the African-American population and this group tends to experience more severe lung problems.
As far as sarcoidosis symptoms go, it depends of what organs are affected and how progressed the disease is. In some people, there are no symptoms, so they dont know they have a problem until they have other testing, such as an x-ray, for some other reason.
Here are some generalized sarcoidosis symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Weight loss
For people who have lung disease or lung-associated problems due to sarcoidosis, symptoms can include persistent dry cough, wheezing, shortness of breath and chest pain. Skin related issues could involve a rash, lesions, color changes or nodules, which are best described as growths just under the skin. They are more likely to form around scars or tattoos.
Are There Alternative Treatments To Corticosteroids
Other treatments are available for patients who cannot tolerate steroids either because they are contraindicated or because side effects cannot be tolerated. Patients whose disease does not respond to steroids or who wish to lower the dose of steroids and use another drug in combination have additional treatment options as well.
You May Like: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
When Is Treatment Started
Many questions exist regarding the appropriate timing and duration of treatment for sarcoidosis. The decision to begin treatment generally depends on the organ system involved and the severity of disease.
There are several situations, however, under which some form of treatment is usually given. These include patients with neurological, heart, and sight-threatening disease those with serious pulmonary symptoms and/or worsening lung function and those with kidney involvement–specifically, hypercalcemia. Because of the serious effects that can occur when these systems are involved, treatment is started even if symptoms are mild.
Other indications for which treatment could be considered include an inability to work as a result of fever, weakness, fatigue, joint pain, nervous system changes, respiratory symptoms , and disfiguring skin disease.
What Can People With Sarcoidosis Expect
In many patients, the disease gets better all by itself. Women and people with less severe lung involvement usually do the best. If you have sarcoidosis, you should discuss your illness in more detail with your family doctor. As with most other illnesses, you and your doctor should work together as partners to ensure the best treatment plan for you and your general well-being.
Don’t Miss: Is Red Wine Good For Kidney Stones
What Is The Life Expectancy Of A Person With Sarcoidosis
In many people, sarcoidosis will go away on its own and never come back.
Less than 5% of people with sarcoidosis die from their disease. Usually, death is because of organ damage or complications of treatment.
People most likely to die from sarcoidosis are those who are older, have extensive pulmonary fibrosis , pulmonary hypertension, or heart or brain involvement.
Sarcoidosis And Ms: Many Similar Symptoms
Neurosarcoidosis and MS could have many of the same symptoms, like these:
- Cognitive changes, like brain fog, forgetting words, or being slow to process new information
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Changes to your gait or movements
- Hearing loss
Similar complications: People with either sarcoidosis or MS could have these serious complications:
- Uveitis, an inflammation of tissue inside the eyeâs wall that causes redness, pain, and blurry vision
- Optic neuritis, an inflamed nerve in your eye that can cause eye pain, blurry vision, or vision loss
- Myelopathy, compression or squeezing of your spinal cord that can cause pain, numbness, or changes in how you move
Similar imaging: People with either neurosarcoidosis or MS can have lesions on their brainâs white matter that show up on imaging tests like an MRI. Your scans may show multiple lesions or spots.
Your radiologist will review your MRI scans carefully to look for differences between lesions that are typical for sarcoidosis or those that are more likely due to MS.
Read Also: Watermelon Is Good For Kidney
How Is Pulmonary Sarcoidosis Treated
Treatment is generally done to control symptoms and improve the function of organs affected by the disease. Steroid medicine, such as prednisone, may help reduce inflammation. It can be taken by mouth or inhaled. Other medicines, such as methotrexate, may be used in severe cases or if steroids dont work.
In many cases, no treatment is needed for pulmonary sarcoidosis. Different treatments work better for different people. Sometimes more than one treatment is used. Most medicines used to treat sarcoidosis suppress the immune system.
You may also join a rehab program that includes education, exercise, and support. In severe cases, which are not common, oxygen therapy and even lung transplant may be needed.
Herbal And Nutritional Supplementation
As Ive already mentioned, people with sarcoidosis have higher levels of inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation doesnt just drive sarcoidosis, but it is also a key driver for most chronic health conditions including cardiovascular disease, diabetes and kidney disease so reducing inflammation is of primary importance for all aspects of health.
Increased formation of reactive oxygen species , resulting in high levels of oxidative stress is also suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis and studies have shown that people with sarcoidosis have reduced antioxidant levels with those with the most severe disease having the lowest antioxidant capacity.
Nutritional and herbal supplements can help to protect against ROS-mediated damage, reduce elevated inflammation and protect the kidneys from damage. Key herbs and nutrients include:
Key antioxidant and anti-inflammatory herbs: Turmeric , Ginger, Boswellia, Rehmannia and Resveratrol.
Key antioxidant and anti-inflammatory nutrients: Omega-3 fatty acids, SPMs , Quercetin, Bromelain, Alpha lipoic acid, Coenzyme Q10, vitamin C, vitamin E and N-acetyl cysteine.
Also Check: Is Vinegar Good For Your Kidneys
Sarcoidosis In Native And Transplanted Kidneys: Incidence Pathologic Findings And Clinical Course
-
Affiliation Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States of America
-
Affiliation Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States of America
-
Affiliation Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States of America
-
Affiliation Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States of America
-
Affiliation Department of Surgery, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States of America
-
Affiliation Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States of America
-
Affiliation Department of Pathology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, United States of America
Progression Of Sarcoidosis And The Kidney
The natural history of sarcoidosis in the kidney is variable, depending on the extent of disease and resulting fibrosis that occurs throughout the disease process. The extent of kidney involvement can be reduced by using steroid treatment in the early stages of disease. The patient may also experience the development of kidney stones on a number of occasions throughout their lives, which may be acutely painful and require surgery or medications to hasten recovery. Deterioration of the condition to renal failure may occur in patients with severe kidney involvement in the disease process.
Recommended Reading: Can Chocolate Cause Kidney Stones
What Is Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a rare disease caused by inflammation. It usually occurs in the lungs and lymph nodes, but it can occur in almost any organ.
Sarcoidosis in the lungs is called pulmonary sarcoidosis. It causes small lumps of inflammatory cells in the lungs. These lumps are called granulomas and can affect how the lungs work. The granulomas generally heal and disappear on their own. But, if they dont heal, the lung tissue can remain inflamed and become scarred and stiff. This is called pulmonary fibrosis. It changes the structure of the lungs and can affect your breathing. Bronchiectasis can also occur. This is when pockets form in the air tubes of the lung and become infected. But, these problems are not common.
What Are Symptoms Of Sarcoidosis When It Affects The Lungs
The lungs are affected in more than 90% of individuals with sarcoidosis. Even in individuals whose disease primarily affects other organs, the lungs are usually affected as well. Shortness of breath, cough, and chest discomfort are the most common lung-related symptoms. Patients may be free of chest symptoms despite an abnormal chest x-ray and biopsy-proven sarcoidosis. Occasionally, patients have chest pain which is usually described as a vague tightness of the chest but sometimes the pain can be severe and similar to cardiac pain.
It’s thought that sarcoidosis of the lungs begins with alveolitis. Alveolitis is inflammation of the alveoli, which are the tiny sac-like air spaces in the lungs where carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged. Alveolitis either clears up by itself or progresses to granuloma formation. Samples of lung tissue may show the presence of granulomas.
Granulomas in the lungs can lead to narrowing of the airways, enlargement of lymph nodes in the chest, and inflammation and scarring of lung tissue. The scarring causes the lung tissue to stiffen and destroys the air sacs, making it more difficult to breathe.
Don’t Miss: Can A Kidney Infection Cause Diarrhea
Key Points About Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
- Sarcoidosis is caused by inflammation. Most cases of sarcoidosis are found in the lungs and lymph nodes, but it can occur in almost any organ.
- Sarcoidosis in the lungs is called pulmonary sarcoidosis. It causes small lumps of inflammatory cells, called granulomas, in the lungs. They can affect how the lungs work.
- The cause of pulmonary sarcoidosis is unknown.
- The most common symptoms of pulmonary sarcoidosis are shortness of breath, which often gets worse with activity dry cough that will not go away chest pain and wheezing.
- Treatment is generally done to control symptoms or to improve the function of organs affected by the disease. Steroids are often used.
How Are Sarcoidosis And Ms Different
In about 90% of people with sarcoidosis, the disease mainly affects their lungs. They have a nagging cough and shortness of breath. Rashes and skin bumps are also common in sarcoidosis. MS doesnât cause coughs or skin rashes.
Also, MS is far more common than sarcoidosis:
- Close to 1 million Americans have MS, much higher than we estimated in the past.
- Itâs estimated that 150,00-200,000 Americans have sarcoidosis.
- Neurosarcoidosis is even rarer. Only 5%-15% of people with sarcoidosis have disease that affects their nervous system.
Racial/ethnic differences: Sarcoidosis is much more common among Black people than white people. MS is more common in white people, particularly people with Scandinavian ancestry, than Black people.
Different disease courses:
- People with MS often have symptoms that come and go for years. This is called relapsing-remitting disease. Later on, most people have symptoms that get worse.
- Some people with milder MS donât need any treatment to manage their symptoms, but most do need treatment to relieve flares or slow down their disease.
- Up to 70% of people with sarcoidosis have symptoms that go away on their own with no treatment, while the other 40% do need treatment. Some people with sarcoidosis can die from its complications unless they start taking medications.
Autoimmune vs. immune-related
Scientists classify MS as an autoimmune disease. Your immune system attacks your own healthy nerves for some reason.
Read Also: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For Your Kidneys
Sarcoidosis And The Joints Muscles And Bones
Sarcoidosis may affect many parts of the body including the joints, muscles and bones. Approximately 1 in 5 patients with sarcoidosis have these musculoskeletal symptoms. This contains more information on the symptoms, tests and treatment for sarcoidosis affecting the joints, muscles and bones.
The information on this page has been compiled with the help of sarcoidosis specialists Dr K. Bechman and Dr J. Galloway, Rheumatology, Kings College Hospital, London.
How Is Sarcoidosis And The Kidney Diagnosed
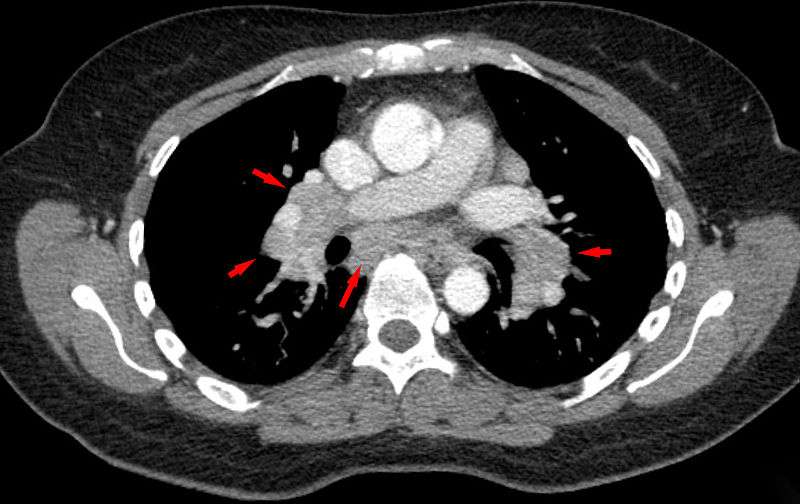
To investigate sarcoidosis renal disease, a number of blood and urine tests may be required to determine the overall function of the kidneys. This will allow assessment of how much damage has been done by the sarcoidosis. If the condition of sarcoidosis has not been previously diagnosed, blood tests and x-rays can be taken to confirm or deny the existence of sarcoidosis.
Also Check: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For Kidney Disease
Statistics On Sarcoidosis And The Kidney
Sarcoidosis is a rare condition with an incidence of 19 per 100,000 population in the United Kingdom. It is more common in the USA but less common in Japan. The course of the disease is more severe in African-Americans than caucasians. Most patients develop symptoms between the ages of 20 and 40 years, with a known medical history of sarcoidosis. Only rarely is kidney disease the cause of the first clinical symptom.
Although most remain without symptoms of renal disease, it is estimated that 15-40% of patient with sarcoidosis have some involvement of the kidneys in this disease process.