Complex Kidney Cyst Complications
Complex kidney cyst has its complications. Its important not to allow starting of inflammatory processes. They often occur in the fluid filling the cyst cavity.
In addition, there may be a hemorrhagic kidney cyst. This occurs when there is bleeding inside the cyst. Blood partially or completely fills the cavities of a complex kidney cyst.
Echinococcosis cyst is extremely unpleasant thing caused by hydatid tape worm. This disease is called hydatidosis.
As a rule, mature worm lives in the small intestine of a dog. Man is a random intermediate master. The most common localization site is the liver. Renal hydatidosis is about 2% of human echinococcal cysts.
Renal cancers account for about 7-10% of cystic lesions detected by ultrasound. Although the percentage is small, the risk of cancer is worth carrying out some additional diagnostic procedures to make accurate diagnose.
Localized Cystic Renal Disease
Localized cystic renal disease is a rare, nonhereditary, form of cystic renal disease, which manifests as a conglomeration of multiple simple cysts of variable size . In contrast to ACKD and ADPKD, localized cystic renal disease is typically unilateral and not progressive. The disease usually involves only a portion of the kidney with a polar predilection . Entire renal involvement is rare . The contralateral kidney is normal. The presence of interposed normal renal parenchyma and the absence of a capsule help to differentiate localized cystic renal disease from cystic nephroma and multiloculated cystic RCC . Cystic involvement of other organs is typically absent .
Fig. 13
Localized cystic renal disease. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows a conglomeration of multiple simple cysts of variable size in the right kidney
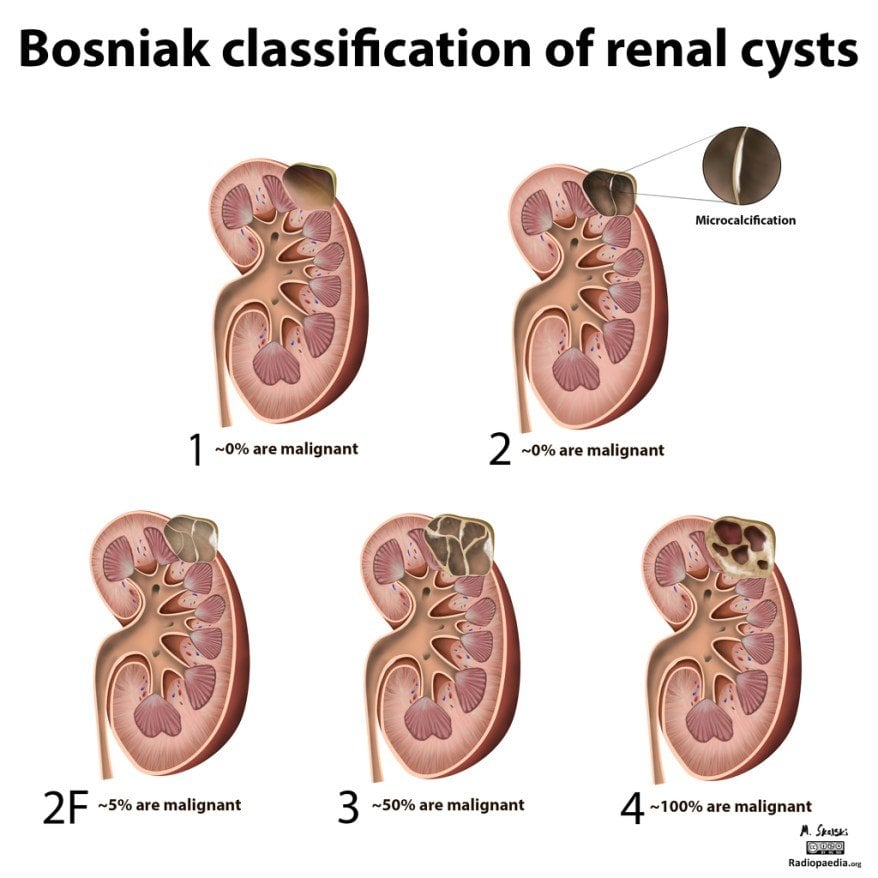
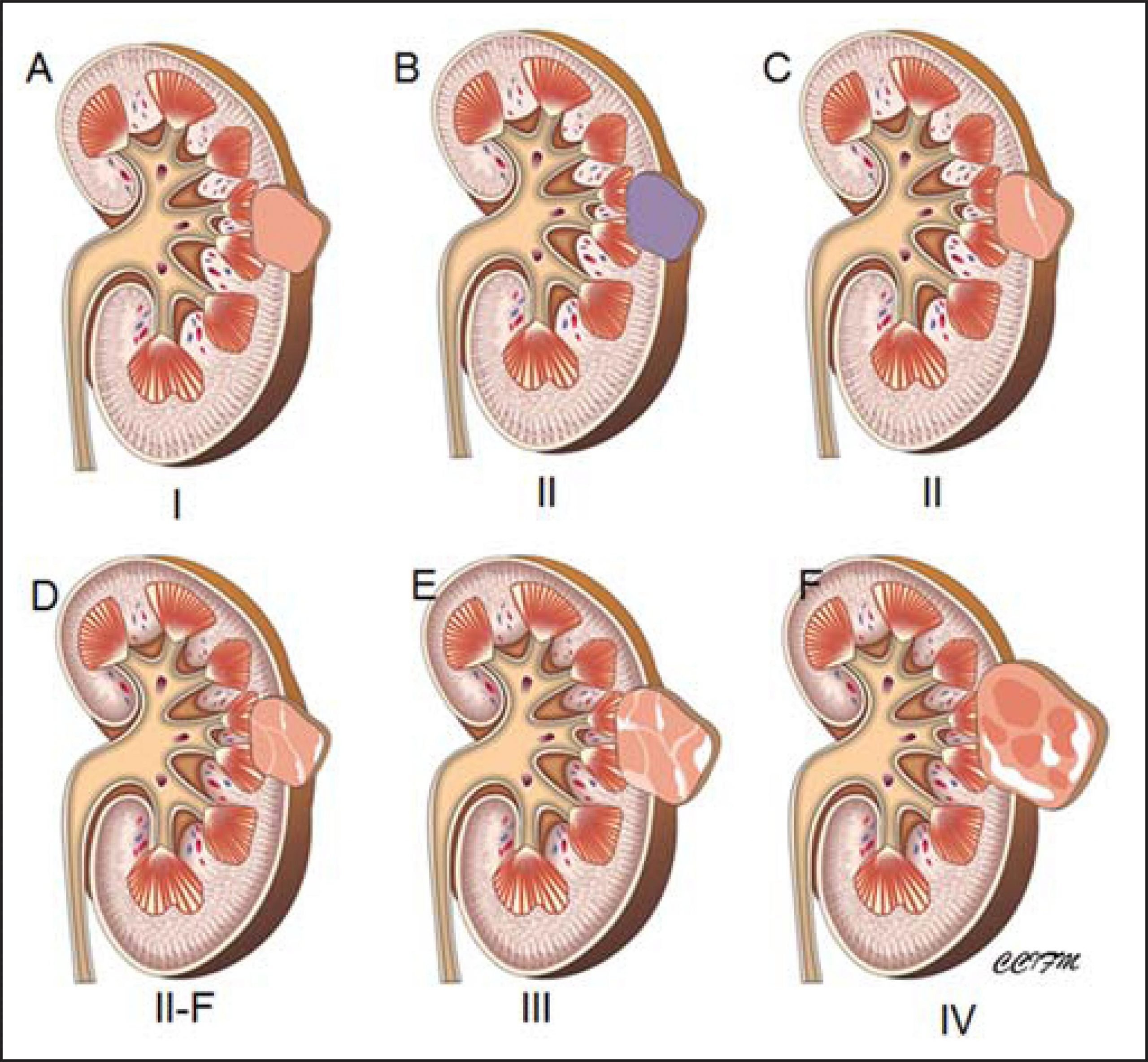
Bosniak Classification System For Renal Cysts
The most widely used system to classify cystic renal lesions was introduced by Bosniak in 1984 and revised in 1997 . This system was originally developed on CT findings, but it can be also used at MRI .
Renal cysts are divided into five categories on the basis of imaging appearance . Each Bosniak category reflects the likelihood of cystic RCC that ranges from I to IV . Category I, II, and, IIF cysts are nonsurgical, while categories III and IV are surgical.
Table 1 The five categories of renal cysts, divided on the basis of imaging appearanceFig. 2
Imaging features of cystic renal lesions according to Bosniak classification. a Bosniak category I cyst: thin wall. b Bosniak category II cyst: thin wall; few, thin septa. c Bosniak category II-F cyst: minimally thickened wall; several, minimally thickened septa. d Bosniak category III cyst: irregularly thickened wall; several, irregularly thickened septa. e Bosniak category IV cyst: enhancing nodularity; irregularly thickened wall; several, irregularly thickened septa
In equivocal cases, another option is to use subtraction MRI to assess the presence or absence of enhancement .
Category I renal cysts
Fig. 3
Bosniak category I renal cyst. Axial non-enhanced and contrast-enhanced CT images shows a cyst with a thin and non-enhancing wall
Category II renal cysts
Fig. 5
Category IIF renal cysts
Fig. 6
Category III renal cysts
Fig. 8
Category IV renal cysts
Fig. 9
Also Check: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Your Liver And Kidneys
What Causes Kidney Cysts
If your kidney cysts are caused by PKD, then they are inherited. This means you have them because they run in your family. For most people, though, this is not the case. Doctors arent sure why kidney cysts form for them. It could be that the kidney surface weakens over time. This could explain why kidney cysts are most common in people who are age 50 and older.
Re: Kidney Complex Cyst
I am not a doctor or any sort of medical practitioner.; I had not heard of this problem before, however, I have done some checking.; One web site states that complex kidney cysts have a low risk for being or becoming a kidney cancer, but should always be evaluated by a Urologist to be certain.; I think that there’s every hope that you will be ok and we’ll all keep our fingers crossed for you.
I imagine that most people on this forum have been through the agonising wait for tests and then the even more agonising wait for results.; Please be reassured that here is a safe place to express your fears and seek reassurance.;
Best wishes
You May Like: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
How Do You Get Rid Of A Cyst On Your Kidney
Options include:
Complex Renal Cyst And Cancer
Simple kidney cysts differ from the complex ones in regularity of shape, cyst lining and internal structure. The complex renal cyst has irregular cyst lining and may show irregular shape and internal structure. The internal walls may divide it into many parts. These walls or the septum inside the complex renal cyst can be thin or thick and coarse. The presence of multiple internal walls give rise to the possibility that the cyst may develop into kidney cancer. Calcification of the cyst is another characteristic of these cysts. A radiology imaging test such as CT scan or ultrasound, can detect the presence of calcium inside the kidney cyst. These tests may also reveal that a part of the cyst is well supplied with blood.
Presence of mass inside the complex renal cyst increases the risk of acquiring kidney cancer. It is a warning that there is some problem and you need to consult a competent urologist about treatment as soon as possible. Your urologist may use Bosniak classification method to judge the risk of a renal cyst transforming into the cancer of kidney. The method depends on the age of molecular biology, appearance of the cyst in the CT scans with contrast, ultrasonography or MRI. According to this method, Bosniak category I, II, III and IV complex renal cysts have 2%, 18%, 33% and 92% chances, respectively, of being linked with kidney cancer. The Bosniak IV complex renal cysts are usually related to kidney cancer.
Don’t Miss: Can Kidney Stones Cause Constipation Or Diarrhea
Evaluation Of Incidental Renal And Adrenal Masses
JAMES C. HIGGINS, CDR, MC, USN, and JAMES M. FITZGERALD, MAJ, USAF, MC, Naval Hospital, Jacksonville, Florida
Am Fam Physician.;2001;Jan;15;63:288-295.
;See patient information handout on kidney cysts, written by the authors of this article.
The widespread use of abdominal computed tomographic scanning and ultrasonography has increased the detection of incidental renal and adrenal masses that are found on imaging for problems unrelated to the kidneys or adrenal glands. Based on careful clinical assessment, imaging studies and selected screening laboratory tests, family physicians can diagnose most of these masses and determine the need for referral.
Understanding The T Word
The term tumor refers to an area in an organ that is not typically supposed to be there. A tumor may also be referred to as a mass, lesion, neoplasm or cyst. All of these terms mean the same thing, but none of them indicate whether or not a tumor is cancer. Often, tumors are found accidentally when an individual is undergoing x-rays for other reasons. Sometimes, they are found when investigating why a patient is experiencing side pain or blood in the urine.
Read Also: Is Mulberry Good For Kidneys
Can A Complex Kidney Cyst Increase The Risk For Renal Cancer
Kidney cysts are closed pockets of tissue, filled with fluid, that develop in the kidneys. Multiple cysts can develop, or a single cyst. Kidney cysts can develop more or less spontaneously with no underlying cause, or they may develop as a result of a condition such as polycystic kidney disease or multicystic kidney dysplasia. The development of so-called âsimpleâ kidney cysts becomes more common in older people: up to 30% of those aged 70 and over have one or more cysts.
Complex kidney cysts are so-called because of their irregular shape. Another difference between simple and complex cysts is that complex kidney cysts often have âenhancedâ tissue, meaning that within the cyst, there is tissue that has access to a blood supply.
Most of the time simple cysts are asymptomatic and are not harmful. Sometimes, they may cause pain if cysts enlarge to the point where they encroach on other organs. In other cases they may become infected or may bleed. It is rare for simple kidney cysts to cause any reduction in kidney function. However, there is a link between simple kidney cysts and high blood pressure, although it is unknown whether the link is a causative link or simply correlation.
What Causes Simple Kidney Cysts
Kidney cysts occur when the tube of a nephron begins to get bigger and fill with fluid. Researchers don’t know what causes this to occur, but they do know that simple cysts aren’t inherited. It is believed that injury or microscopic blockages in the tubules may lead to the development of some simple kidney cysts.
Recommended Reading: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
Coalition For The Reversal Of Breast Cancer Mortality In African American Women
A blog about research, awareness, prevention, treatment and survivorship of Breast Cancer and all cancers, including targeted scientific research and a grassroots approach to increase screening for cancer, especially in the low income and under-insured population of El Paso, Texas, with a view to expand this new health care model to many other ‘minority’ populations across the United States and beyond
Should I Get A Biopsy
A question that we hear all the time. There is a theoretical risk of bleeding or spreading the cancer with a biopsy, but this not why they are not widely used.
Unlike prostate, breast, or colon biopsies it turns out that biopsies of small kidney tumors are not as accurate as we would like.
As many as 20% of the biopsies are “false negatives”- in other words the biopsy says there is no cancer when indeed there is a cancer.
We still use them sometimes but it has to be in the right patient. Recent innovations in how we do the biopsies has allowed us to get more information than ever before. It remains, however, that a biopsy should only be obtained after a discussion with an expert on this disease!
Treatment options for patients with a small kidney tumor including active surveillance, ablation, partial nephrectomy, and total nephrectomy. In the vast majority of patients treatment of a small kidney tumor should result in saving the kidney. A quick decision to remove the kidney may not be the best treatment. Experience is critical in being able to save the kidney. In our section regarding treatment one can find details regarding these options.
At Johns Hopkins our surgeons are experts on all approaches and will help tailor the treatment to the patient. One size does NOT fit all.
Recommended Reading: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Your Liver And Kidneys
Lesion Size And Bosniak Category
There were no Bosniak category I lesions. Also, there was no RCC in Bosniak category II . RCC appeared in 3 of 18 cases in category IIF, 21 of 39 cases in category III, and 29 of 32 cases in category IV.
The mean size of benign cysts did not differ significantly from that of RCC . However, the mean size of each Bosniak category differed significantly in an increasing manner .
Causes Of Complex Kidney Cysts
A complex kidney cyst can develop as a secondary manifestation of a simple cyst. Such relapse occurs as a result of complications such as infection or bleeding, and also as a result of the proliferative process .
As is the case with simple kidney cyst formation, different types of complex kidney cyst can give similar pictures on medical ultrasound diagnosis. Therefore, it is not possible to make an accurate diagnosis without additional examinations.
However, the timely detection of a complex kidney cyst with using ultrasound is already important in the successful treatment. Features indicating the presence of cystic formation during ultrasound diagnostics:
thickening and irregular contour of the cyst wall ;
presence of partitions;
the presence of seals or solid elements in the tissues present in the plural;
distinct vascularization .
Also Check: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
Kidney Cysts And Polycystic Kidney Disease
Kidney cysts are fluid filled sacs that can form on the outside or inside of a kidney. Termed simple cysts, they are benign and generally cause little to no trouble. More complicated cysts can interfere with kidney function, or create other complications. Complex kidney cysts require close radiographic imaging , or surgical removal since these cysts can be cancerous.
Kidney cysts are relatively common, and the incidence of forming cysts increases with advanced aging. Kidney cysts may also be part of a genetic disease that results in a slow, progressive decrease in kidney function. In this scenario, there is usually a family history of kidney disease. A kidney cyst diagnosis may involve the presence of one or more cysts. Polycystic kidney disease involves numerous cysts that cover one or both kidneys.
Referral Of Patients With An Incidental Adrenal Mass
Referral is required for patients with an incidental adrenal mass larger than 3 cm if a change in the size of the lesion is noted on serial radiographic studies. Referral for surgical removal is required for all patients with adrenal masses larger than 6 cm because of the possibility of malignancy. Patients with masses between 3 and 6 cm in greatest diameter should undergo an MRI study and additional endocrine evaluation; referral may be advised.
Patients with abnormal screening laboratory results should be referred, regardless of the size of the mass, because hormone-producing tumors need to be surgically excised. Lastly, all patients with a history of a malignancy who are found to have an adrenal mass probably should undergo needle biopsy of the lesion because metastatic disease is the most likely pathology in this situation.19
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Three Main Regions Of The Kidney
Ct Or Mri: Advantages And Disadvantages
Contrast-enhanced CT is the modality of choice in evaluating cystic renal masses. Narrow detector thickness and intravenous administration of contrast agent are mandatory to detect thin septa and small enhancing nodules . Also, demonstration of enhancing areas helps differentiate solid components from hemorrhage or debris . MRI is used when CT is contraindicated or as a problem-solving modality for equivocal findings. Indeed, MRI can show some septa that are less apparent at CT and demonstrate definitive enhancement in those cysts that show only equivocal enhancement at CT . As a consequence, renal cysts can be placed in a higher Bosniak category with MRI than with CT .
Kidney Tumor With Suspicion Of Spread
You may have been told that the kidney cancer has spread. This could be to lymph nodes, the lungs, liver, bone, or even the vena cava â the largest vein in your body.
About 1/3 of patients find that the cancer has spread even without any symptoms.
For those with symptoms, you may have experienced abdominal or back pain, blood in the urine, bone pain, seizures, or even bad headaches. After a full evaluation of the extent of spread a treatment plan should be formulated.
This can get quite complicated and a multidisciplinary team who specialize in kidney cancer would be best to help with this. It is important that an urologist and medical oncologist collaborate in constructing an optimal plan for your care. This multidisciplinary approach is most important for cancers with a high suspicion of spread! This is because today there are numerous options and combinations for patients with metastatic kidney cancer.
These options can include:
Surgery – In certain settings, removal of the kidney even when the cancer has already spread has been shown to improve survival. This can often be done laparoscopically so the patient can recover rapidly and promptly receive additional therapy.
Immunotherapy – IL-2 can be a good option for some patients and can deliver excellent results for some patients. Interferon-alpha is another option.
Recommended Reading: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Symptoms Of Complex Renal Cyst
Most of the time complex renal cysts are asymptomatic; they are accidently detected while doing sonography for some other disease. However few of them can present with symptoms due to rise in the size and infection, leading to internal pressure on the kidney.
- Hematuria: blood in urine. Due to over distension, one of the cyst can rupture into the renal pelvis and causes bleeding.
- Dull and throbbing pain in the abdomen, either due to increased weight of the kidney, or due to tension within the cysts. Sometimes the pain mimics as that or a renal stone.
- Vomiting, fever and nausea may be felt in some individuals where the cyst gets infected.
- Enlarged size of kidney: the large knobby kidney can be discovered in the course of a routine examination by a physician.
- Urine protein: Most of the time there will be no excess of protein loss from the urine, which can cause nephritic syndrome.
How Should Patients With Renal Cell Carcinoma Be Managed
Surgery
Laparoscopic or open approach depends on the nature of the tumor and surgeon preference and expertise:
-
Partial nephrectomy- limited resection of the portion of the kidney where the mass is
-
Simple nephrectomy- removal of the kidney without node or adrenal resection
-
Radical nephrectomy- includes a perifascial resection of the kidney, perirenal fat, regional lymph nodes, and ipsilateral adrenal gland
-
Cytoreductive nephrectomy- removal of the kidney in the setting of advanced stage IV disease where cure is not expected to be achieved
Surgical resection of localized disease remains the treatment of choice for either cure or long-term disease-free survival. Nephrectomy is recommended in patients with stage I-III disease. The degree of resection is dictated by the extent of disease and location of the tumor. Historically, partial resection was done in patients with a solitary kidney or severe CKD where a radical nephrectomy would render a patient functionally anephric. With recent data suggesting that nephrectomy-induced CKD is associated with an increased risk of all-cause and cardiovascular death, nephron-sparing procedures should be considered when at all possible.
Summary of surgical recommendations based on TNM stage of disease
Ablation Therapy
These procedures are performed by urologists and interventional radiologists. They are generally performed under conscious sedation but may require general anesthesia.
Immunotherapy
Targeted Molecular Therapy
Surveillence
Recommended Reading: How Much Money Is A Kidney Worth