How We Make Abo Incompatible Transplants Successful
We are one of the nation’s leading centers for transplants performed between incompatible blood type donor and recipient pairs. More than 30% of the living donor transplants we perform are ABO incompatible. Our success rates for these transplants are nearly equal to compatible blood type transplants.
Our approach to handling these complex cases includes:
Innovative Immune Modifying Techniques
The recipient will naturally have antibodies in their blood that will attack a kidney from a donor with a different blood type. It’s crucial to reduce the levels of these antibodies prior to transplant surgery. We use several advanced techniques to successfully modify the recipient’s immune system and block these antibodies.
Careful Monitoring
We continuously test the antibodies in your blood as we prepare you for surgery. We schedule the transplant when the techniques have been successful and your antibody level has decreased.
Post-Transplant Care
All transplant patients need to take immunosuppressant drugs to keep their body from rejecting the new organ. But after an ABO incompatible transplant, monitoring for rejection is even more critical. The team at Cedars-Sinai is pioneering the use of new medications that can significantly reduce rejection caused by antibodies.
Positive Crossmatch And Sensitized Patients
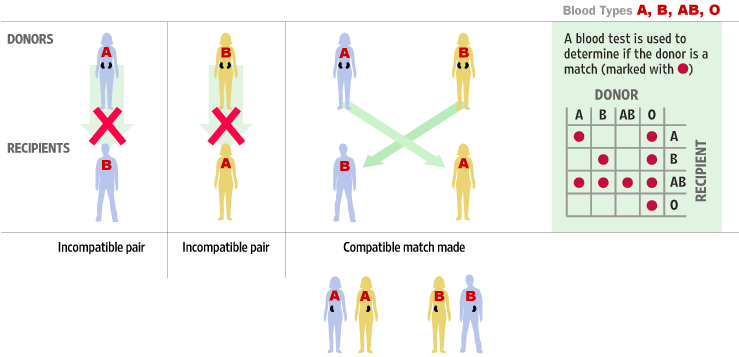
About 30% of transplant patients are sensitized. This means that they have harmful antibodies which will attack foreign tissue, such as the transplanted organ from a living donor. These antibodies develop through a previous exposure to foreign tissue, such as through pregnancy, previous transplants, or blood transfusions. Sensitized patients may wait three to four times longer than unsensitized patients for a compatible deceased donor kidney.To test a recipient for these antibodies, a sample of their blood is mixed with a sample of the potential donors blood. This test is called a crossmatch, and shows how a recipients antibodies react with the potential donors. Test results can be either positive or negative. It may seem confusing at first, but a positive crossmatch means that a donor and recipient are not compatible.
A positive crossmatch results in the recipients antibodies attacking the donors which means the kidney is not suitable for transplant.
A negative crossmatch means that the recipients antibodies do not attack the donors which means the kidney is suitable for transplant.
What Are Antibodies And How Does Rejection Occur
Antibodies are proteins your immune system makes when it comes into contact with something foreign to your body. When you get an infection, such as a cold or an infection from a wound, your body makes antibodies to fight that infection. Antibodies protect your body. When you have an organ transplant, your body reacts as it would to an infection. Thus, your antibodies try to destroy the organ. Some people have a lot of antibodies, and it is harder to find an organ match.
You May Like: Whats Renal
Why Compatible Pairs Can Benefit From Using The Nkr
Paired exchangewhen a donor donates their kidney to another recipient in exchange for a compatible, or better-matched, kidney for their loved onewas originally created to overcome cases of donor-recipient incompatibility, when the donor could not give directly to the intended recipient.
However, compatible pairsdonor-recipient pairs where the donor can donate directly to the patientcan also greatly benefit from entering paired exchange.
Through paired exchange and the Kidney for Life initiativewhich utilizes the latest generation in DNA sequencing technology to assess the histologic match between patients and donorscompatible pairs can find excellent matches, and the recipient can potentially reduce their immuno-suppression dosage and have a transplanted kidney that lasts longer.
What Are The Common Matching Factors
Blood type and body size factor into a match.
Other factors include:
- how bad the patients medical condition is
- the distance between the donor’s and the patients hospital
- the patient’s waiting time and
- if the patient is available. For example:
- If they cant contact the patient.
- If the patient has an infection or other reason that they cant do the transplant.
The most important factor is the organ itself. Some organs can survive outside the body longer.
Theres a different policy for each organ. Read about how the system decides who gets which organs.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have 4 Kidneys
Living Kidney Donation Is Safe
If you are healthy, donating a kidney wont make you more likely to get sick or have major health problems. Like any surgery, the procedure does have some risks. But overall, living kidney donation is safe. In most cases, donating a kidney will not not raise your risk of kidney disease, diabetes, or other health problems.
What Does It Mean When Your Kidneys Are Not Working
If your kidneys are not working properly some or all of these functions may be affected. Chronic kidney disease or CKD means that your kidneys are not working properly. Chronic means it is long term. Visit the My Kidney website for more information about chronic kidney disease, the stages of kidney disease and possible treatment options.
Don’t Miss: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Affect Your Kidneys
How Long Will I Be On The Kidney Transplant Waitlist
Once you register to be on the kidney transplant waitlist, there may be a considerable wait. There are approximately 95,000 people on the waitlist list and the average wait time for a deceased kidney is 3 to 5 years. You can get on the waitlist for a kidney transplant when your GFR is 20 or belowbefore kidney failure. The sooner you can get on the list, the better.
The United Network for Organ Sharing manages the national list of people waiting for an organ transplant. Transplants are generally more successful when the transport time for an available kidney to the transplant facility is as short as possible. So, the UNOS matching system also factors in the distance between donor and the transplant center when selecting a match. If you live in an area with access to more than one transplant center, it is recommended that you get screened and accepted at as many transplant centers as possible in order to have a greater chance of finding a kidney donor sooner. Different transplant centers have different requirements for accepting transplant patients.
What Are The Types Of Kidney Transplants
There are two types of kidney transplants: living donor and deceased donor transplants.
- Living donortransplant: the kidney comes from someone who is still alive. Living donors are usually relatives or friends of the recipient but theyneed not be strangers can donate too. People can live healthy lives with just one kidney, so someone who has two may decide to donate one to someone who needs it.
- : the kidney can come from someone who has just died. There are two types of deceased donations: donation after brainstem death or donation after circulatory death .
Don’t Miss: Mayo Clinic Kidney
Where Can I Find More Information On Paired Exchange Programs
If you are interested in a paired exchange program:
What Is A Paired Kidney Exchange
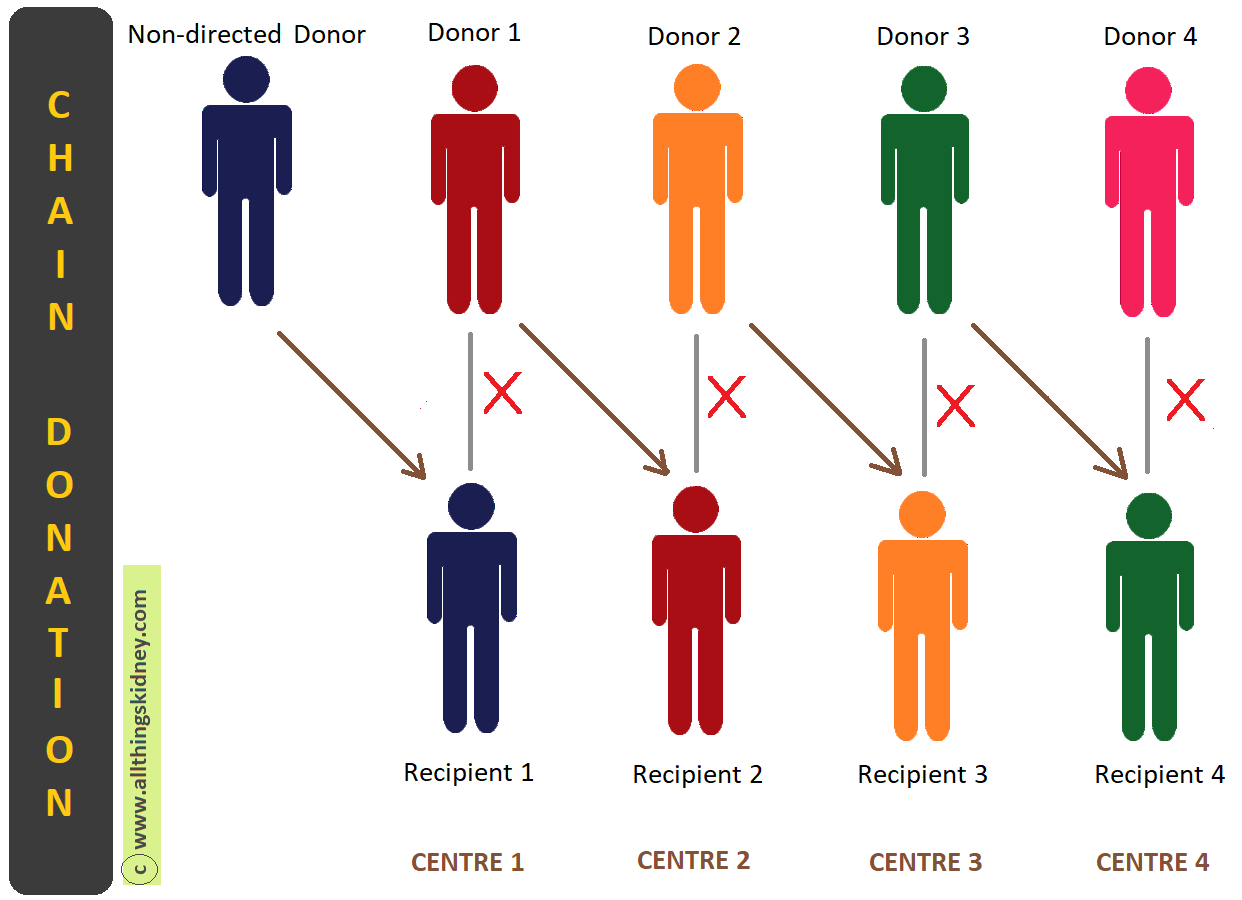
Since 2001, Johns Hopkins Comprehensive Transplant Center has participated in paired kidney exchanges. A paired kidney exchange, also known as a kidney swap occurs when a living kidney donor is incompatible with the recipient, and so exchanges kidneys with another donor/recipient pair. Two live donor transplants would occur. Suppose there were two donor/recipient pairs, Donor and Recipient 1 and Donor and Recipient 2:
- Donor 1 would give a kidney to Recipient 2.
- Donor 2 would then give a kidney to Recipient 1.
This kidney paired donation transplant enables two incompatible recipients to receive healthy, more compatible kidneys. All medically eligible donor/recipient pairs may participate in the paired kidney exchange program.
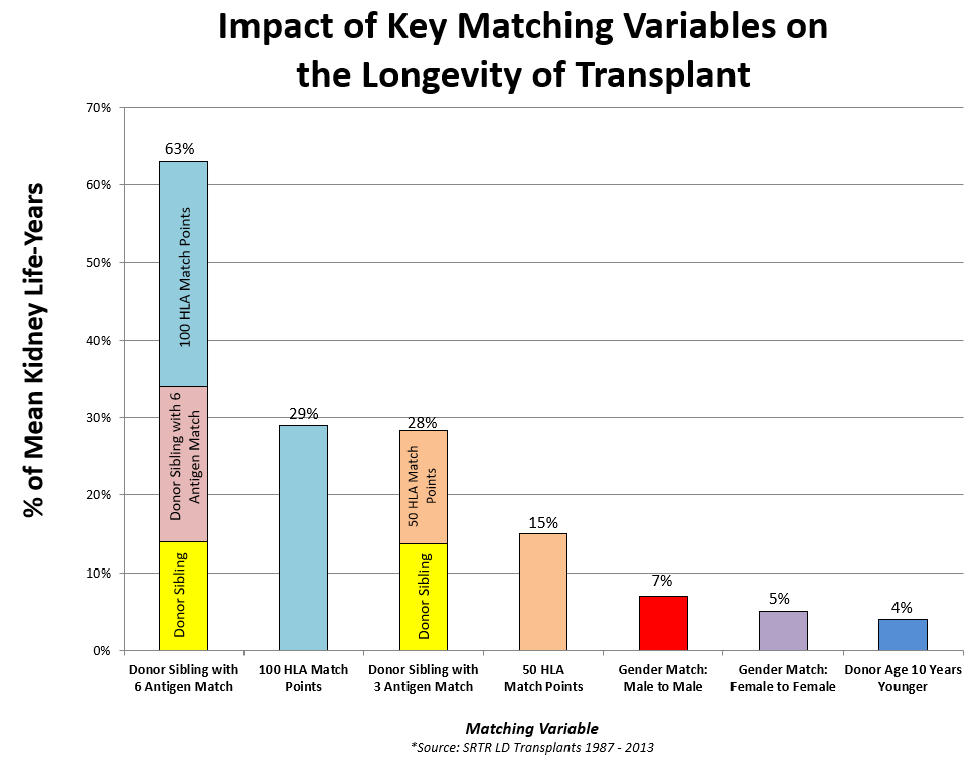
In more complex cases, additional donor/recipient pairs may be used. Participating in the paired kidney exchange program allows for a recipient to receive a better matched kidney, and helps other individuals who would otherwise continue to wait for a matched donor. Approximately 45% of donor/recipient pairs could find a perfectly matched donor by entering the national paired kidney exchange program.
Don’t Miss: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
How Long Does The Process Take
The donation process depends on how many tests are required of the donor and how quickly he or she is able to complete them. The average donor work up may take six months or more for completion and may depend on test results, which may indicate additional evaluation is required. A transplant date cannot be set until the donor has completed the entire work up and has been evaluated by the surgeon. The transplant center does its best to accommodate the needs of the donor and recipient, but appointment times may be limited.
How Do I Know If My Kidney Is A Match For The Recipient
The transplant team will check your blood type as well as the recipient blood type to see if they are compatible. A unique blood test also needs to be done which is called crossmatch.
It is possible that the recipient of the kidney has an allergy to the donated kidney so the recipient’s body may reject the donated kidney. Such allergy is due to some substances called antibodies which are present in the recipient’s blood. In order to make sure that the recipient does NOT have those antibodies against your kidney tissue, the crossmatch test is performed. Briefly, a sample of your blood is combined with a sample of the recipient’s blood. If the recipient has antibodies to the donor, this will cause a “positive” reactivity during the crossmatch test. This may mean your recipient is incompatible to you. In the case that you and your recipient are not compatible, you may participate in UCLA’s Kidney Exchange Program. This program allows the recipient and donor to enter a paired exchange registry, where the donor will donate to another recipient that is matched, and the recipient will recieve a matched kidney from a compatible donor in return.
Also Check: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
Living Donor Kidney Transplantation
Living donor kidney transplants are the best option for many patients for several reasons.
- Better long-term results
- No need to wait on the transplant waiting list for a kidney from a deceased donor
- Surgery can be planned at a time convenient for both the donor and recipient
- Lower risks of complications or rejection, and better early function of the transplanted kidney
Any healthy person can donate a kidney. When a living person donates a kidney the remaining kidney will enlarge slightly as it takes over the work of two kidneys. Donors do not need medication or special diets once they recover from surgery. As with any major operation, there is a chance of complications, but kidney donors have the same life expectancy, general health, and kidney function as most other people. The kidney loss does not interfere with a woman’s ability to have children.
Potential Barriers to Living Donation
- Age < 18 years unless an emancipated minor
- Uncontrollable hypertension
- Bilateral or recurrent nephrolithiasis
- Chronic Kidney Disease stage 3 or less
- Proteinuria > 300 mg/d excluding postural proteinuria
- HIV infection
- Shorter recovery time in the hospital
- Quicker return to normal activities
- Very low complication rate
The operation takes 2-3 hours. Recovery time in the hospital is typically 1-3 days. Donors often are able to return to work as soon as 2-3 weeks after the procedure.
Recovering From The Transplant Surgery
- After the transplant surgery, you will recover in the hospital where you will be watched closely. You will usually spend several days recovering in the hospital.
- In some cases, you may start making your own urine right away. Sometimes, especially with deceased donor kidneys, this will take a bit of time. If your new kidney is not producing urine right away, you will need to stay on dialysis until this starts happening.
- Your transplant team will adjust your immunosuppressant medicines, and watch you closely for signs that your body is accepting the new kidney.
- Usually the transplant team will recommend that you get up and start slowly moving around one day after your surgery.
- Once you have recovered enough to safely go home, you will be released from the hospital and continue recovering at home.
Also Check: Can Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
Your Blood And Tissue Type Must Be Compatible With Your Recipients
Besides being healthy, living donors must have compatible blood and tissue types with the kidney recipient. The transplant team will perform tests to see if your blood and tissues are compatible with the kidney recipient. If they arent, our living donor program can also educate you about the paired donation program.
Does It Hurt To Donate Kidney
After leaving the hospital, the donor will typically feel tenderness, itching and some pain as the incision continues to heal. Generally, heavy lifting is not recommended for about six weeks following surgery. It is also recommended that donors avoid contact sports where the remaining kidney could be injured.
Read Also: Va Rating For Stage 3 Kidney Disease
Is It Normal For A Mans Kidney Function To Decline
This is known as the glomerular filtration rate, or GFR. With time, many mens kidneys start to slip, but function must decline quite a lot before you start to really feel the impact. You feel fine up to the point that kidney function is almost gone, which means you can lead a normal life with reduced kidney function.
How Does The Nkr Find The Best Donor
Traditionally, kidney transplant matches were measured by an HLA match score from zero to six, with six being the best. HLA scores are generally based on A, B and DR antigens. An antigen mismatch is where rejection often starts.
Behind antigens are eplets, which are essential components of HLA epitopes recognized by antibodies. Eplet mismatch analysis has been proven to be a more precise measure of a donor-recipient match compared to antigen matching.
- Reduce the risk of de novo DSA formation
- Lower the probability of rejection
- Lower the probability of graft failure
- Lower their immune-suppression dosage
The National Kidney Registry can help you find a better-matched living donor kidney. Transplants facilitated through the NKR have a lower failure rate at three, five and seven years post-transplant.
Also Check: Does Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
Finding A Kidney Donor
Once your doctor has determined that youre a good candidate for a kidney transplant, youll need to be matched with a kidney donor who is compatible with you in tissue and blood type. There are several ways to go about finding a kidney donor.
Is It Possible To Decrease The Chances Of My Child Developing Antibodies To My Mismatched Numbers If They Were To Have A Deceased Donor Kidney First
What we can do is to put your child on-call for a new kidney, but only accept a kidney with your mismatched numbers excluded.
For example:
If you are: 1 2 3 4 5 6 and your child is: 1 2 3 7 8 9 then we can ask UK Transplant to put your child on-call, but not offer any kidney that has numbers 4,5 or 6.
Your child should not then make antibodies to any of your mismatched numbers but we can never guarantee this.
Blood may need to be given at the time of the transplant, and as blood cells also carry these numbers and the blood may have come from several different donors, your child may make antibodies to them. Some antibodies also react with more than one HLA number.
Also Check: Can Kidney Stones Cause Constipation Or Diarrhea
Am I Eligible To Become A Kidney Donor
You need to undergo a comprehensive evaluation if you decide to donate one of your kidneys to a family member such as your spouse, children, siblings, and parents or to a friend or altruistically to a stranger. You are NOT eligible to become a kidney donor if the doctors assessment suggests that kidney donation is not safe for you.